تاثیر فعالیت های بازاریابی بر کیفیت رابطه در بخش بانکی مالزی

19,300 تومانشناسه فایل: 6436
- حجم فایل ورد: 283.2KB حجم پیدیاف: 507.7KB
- فرمت: فایل Word قابل ویرایش و پرینت (DOCx)
- تعداد صفحات فارسی: 28 انگلیسی: 10
- دانشگاه:College of Economics and Administrative Sciences, Alzaytoonah University of Jordan, P.O. Box 130, Amman 11733, Jordan
- ژورنال: Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services (4)
چکیده
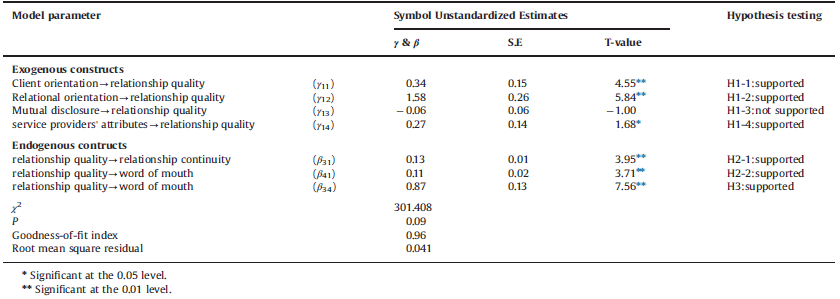
مطالعه حاضر به بررسی تاثیر فعالیت های بازاریابی بر کیفیت رابطه در بخش بانکداری مالزی می پردازد. تجزیه تحلیل نتایج حاصل از نظرسنجی نشان می دهد که گرایش نسبتی کارکنان و مشتریان موجب افزایش کیفیت و تداوم رابطه می شود. هم چنین نتایج نشان می دهد که روابط تعهدی با مشتری منجر به رضایت مشتری، وفاداری و پیشرفت می شود. با این وجود، افشای متقابل هیچ گونه رابطه معناداری با کیفیت ارتباط ندارد. این می تواند نشان دهنده این باشد که مشتریان بانک در مالزی احساس نمی کنند که دارای ارتباط نزدیکی با بانک دارند و هر گون تاثیر مثبتی بر کیفیت رابطه ندارد. این یافته خاص می تواند به عنوان یک سیگنال هشدار دهنده برای متخصصان و محققان باشد که از بازاریابی رابطه در مطالعات خود استفاده کنند.
مقدمه مقاله
رقابت شدید در میان بانک های تجاری به این معنی است که حتی نوآورترین محصولات و خدمات نیز توسط رقبا تکرار می شوند، که بانک ها را از عملکرد در رسیدن به مزیت رقابتی پایدار (SCA) منع می کند (Gordon et al., 2008). محیط بانکداری مالزی از این قاعده مستثنی نیست. بر اساس گزارش Negara Malaysia (بانک مرکزی مالزی)، 23 بانک تجاری مجاز در کشور وجود دارند (http:/www.bnm.gov. my). از این تعداد، ده موسسه دولتی داخلی و 13 موسسه خارجی می باشند. این بانک ها خدمات و محصولات مشابهی را به مشتریان خود عرضه می کنند. رقابت میان این بانک، آنقدر زیاد است که محصولات جدید و خدمات، طول عمر بسیار کوتاهی دارند زیرا توسط بانک های رقیب به شدت کپی برداری می شوند (http: /www.mifc .com). تلاش هایی توسط برخی از این بانک ها برای برای فراتر گذاشتن پا از محصولا اصلی با تاکید بر بازاریابی رابطه مند صورت گرفته است. با این حال، با توسعه اینترنت و کاربرد رایانه، بانک های مالزی بر فراهمی و ارائه خدمات بانکداری الکترونیکی برای مشتریان روی آورده اند. اگرچه این روند با اقتصاد دانش همخوانی دارد، اعتقاد بر این است که بانک های مالزی، بانکداری الکترونیکی را به قیمت بانکداری سنتی مشتری محور انجام می دهند زیرا بانکداری الکترونیکی منجر به افزایش فاصله بین عرضه کننده و مشتریان می شود و از این روی بازاریابی رابطه مند ضعیف تری را ایجاد می کند (Al-alak and Alnawas, 2010). از آن جا که اکنون بانکداری الکترونیکی به صورت استاندارد شده است، بانک ها باید به فکر روش هایی برای بهبود رابطه خود با مشتریان از طریق فعالیت های بازاریابی نسبتی بر خلاف فعالیت های بازاریابی معاملاتی باشند.
از آن جا که بری (1983)، مفهوم بازاریابی رابطه مند را عنوان کرد، بسیاری از محققان (Gronroos, 1990, 1994; Gordon et al., 2008; Palmatier et al., 2009) اقدام به نظریه پردازی و آزمون تجربی اصول اساسی تئوری بازاریابی رابطه مند کرده اند. ایجاد یک رابطه بلند مدت پایدار و سودمند با مشتریان (de Wulf et al., 2001)، افزایش نگهداری مشتریان، توسعه و افزایش رابطه و اعتماد بین فروشنده ها و مشتریان، (Gaur and Xu, 2009)، دستیابی به رضایت مشتری بیشتر و وفاداری مشتری بالا (Gaurav, 2008)، کاهش هزینه ناشی از درک بهتر نیاز های مشتری (Ndubisi, 2004) و افزایش استفاده از برنامه های بازاریابی وفاداری برای تقویت رابطه بلند مدت سود آور با مشتریان که منجر به رشد می شود (Ferguson and Hlavinka, 2007)، برای تئوری بازاریابی رابطه اساسی می باشد. کاربرد تئوری بازاریابی رابطه به دلیل سیاست مقررات زدایی (Yavas and Yasin, 2001)، حذف محدودیت های بین بانک، جوامع و شرکت های بیمه (Speed and Smith, 1992) و افزایش استفاده از فناوری های اطلاعاتی (Bergeron et al., 2008) افزایش پیدا کرده است.
اخیرا در خصوص افراط در برنامه های بازاریابی رابطه مند مبتنی بر فناوری اطلاعات سر و صدای زیادی به پا شده است، زیرا این برنامه ها، اساس بازاریابی رابطه مند را به خطر انداخته اند یعنی خدمات رو در رو، شخصی بین عرضه کننده ها و مشتریانی است که موجب افزایش رضایت مشتری می شود (Eisingerich and Bell, 2006). به علاوه بخش بانکداری به بلوغ خود رسیده است و ناتوانی اکثر بانک های تجاری برای تمیز محصولات و خدمات خود موجب شده تا بانک ها راهبرد های بازاریابی رابطه مند را بر خلاف روابط معاملاتی دنبال کنند(Jham and Khan, 2008). این برنامه از راهبرد های معاملاتی به راهبرد های نسبتی تغییر کرده و بانک ها را ملزم به سرمایه گذاری در راهبرد های بازاریابی رابطه مند کرده است (Claik and Balta, 2006). در خصوص بانکداری الکترونیکی، بانک ها به بررسی عوامل موثر بر بانکداری الکترونیکی برای تحلیل راهبرد های مناسب با هدف رفع نیاز ها و خواسته های کاربران و دست یابی به سطوح بهتر رضایت مشتری و وفاداری بیشتر پرداخته اند (Poon, 2008).
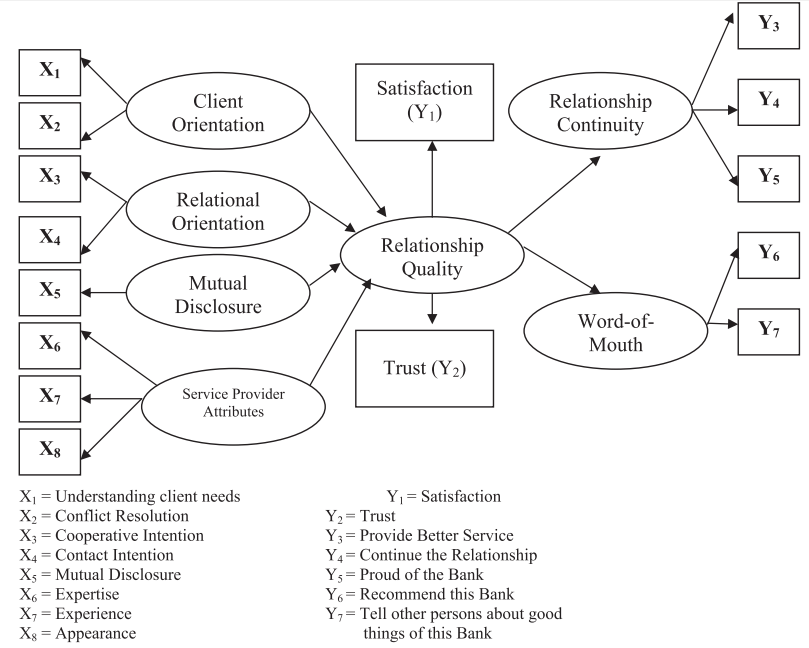
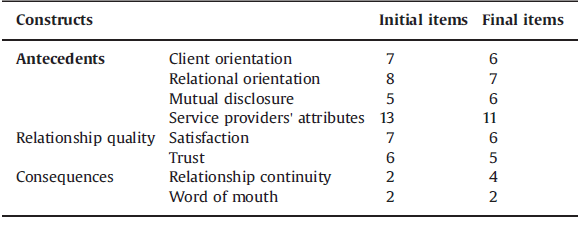
لذا، هدف این مقاله بررسی فعالیت های بازاریابی موثر بر کیفیت رابطه بین کارکنان های بانک های مالزی و مشتریان و عملکرد های متاثر از کیفیت رابطه می باشد. انتظار می رود که هر چه فعالیت های بازاریابی رابطه مند نظیر گرایش مشتری، گرایش نسبتی و افشای متقابل و نیز نسبت های عرضه کننده خدمات مالی بیشتر باشد، کیفیت رابطه بین عرضه کننده های خدمات مالی و مشتریان بالاتر خواهد بود. با افزایش کیفیت رابطه ای، اثر معنی داری بر روی رفتار مشتریان با افزایش تداوم رابطه و کفت و گو اعمال می شود. با این حال، لازم به ذکر است که اگرچه اکثریت مطالعات هدفشان ایجاد رابطه ای بین کیفیت رابطه ای بالا و افزایش تداوم رابطه می باشند، عوامل دیگری وجود دارند که بر مدت زمان رابطه اثر می گذارند. وجود وفاداری رفتاری و یا وفاداری ساختگی در منابع علمی خدمات مالی مستند شده و مستلزم مطالعات بیشتری است.
این پژوهش نقش مهمی در ادبیات بازاریابی بانکی ایفا می کند زیرا این تنها مطالعه برای گسترش کیفیت رابطه در زمینه بانکداری مالزی است. مطالعه فعلی نیز به ادبیات بانکداری کمک می کند، زیرا برخی مفاهیم مدیریتی را ارائه می دهد. نتایج و توصیه های این مطالعه می تواند به مدیران در افزایش درک بهتر عوامل موثر بر بهبود بازاریابی رابطه و بانکداری متقابل کمک کند. این به نوبه خود به فرایند تصمیم گیری و فرمولاسیون استراتژی کمک می کند.
ABSTRACT Impact of marketing activities on relationship quality in the Malaysian banking sector
The current study investigates the impact of marketing activities on relationship quality in the Malaysian banking sector. Analysis of survey results show that greater client and employees’ relational orientation yields higher relationship quality and results in better relationship continuity. Results also show that committed client relationships lead to client satisfaction, loyalty, positive word of mouth and promotion However, mutual disclosure was found to have no significant relationship with relationship quality.This may indicate that bank customers in Malaysia do not feel that having close relationships with the bank will have any positive impact on relationship quality. This particular finding may serve as a warning signal to practitioners and scholars alike that thorough research must be carried out on the use of relationship marketing prior to implementation.
Introduction
Fierce competition among commercial banks has meant that even the most innovative products and services are duplicated by rivals, thus denying banks the opportunity to maintain sustainable competitive advantage (Gordon et al., 2008).The commercial banking environment in Malaysia is no different. According to Bank Negara Malaysia (Central Bank of Malaysia) there are 23 licensed commercial banks in the country (http:/www.bnm.gov. my).Of these banks, ten are Malaysian-controlled institutions, and thirteen are foreign-controlled institutions. These banks offer almost identical (standardized) products and services to their clients. Competition among these banks is fierce to the extent that innovative products and services have very short life cycle, as they are often copied by rival banks (http:/www.mifc.com). Attempts have been made by some of these banks to go beyond the core bank product and service by concentrating on what is called relationship marketing.However, with the proliferation of internet expansion and computer usage, Malaysian banks have been concentrating on the provision of e-banking services to clients. Although this trend is in harmony with knowledge economy, it is believed that obsession with e-banking by Malaysian banks is done at the expense of client-oriented traditional banking, as e-banking widens the gap between service providers and clients, thus resulting in much weaker relationship marketing (Al-alak and Alnawas, 2010).As e-banking services are getting standardized already,banks have to think of ways and means of enhancing their relationships with clients through innovative relational marketing activities as opposed to transactional marketing activities.
Since Berry (1983) introduced the concept of relationship marketing, many scholars and researchers (e.g. Gronroos, 1990, 1994; Gordon et al., 2008; Palmatier et al., 2009) have theorized and empirically tested the underlying principles of relationship marketing theory. Building a profitable and sustainable long term relationship with customers (de Wulf et al., 2001), increasing customers retention, developing and maintaining trust and commitment between sellers and customers (Gaur and Xu, 2009), achieving more customers satisfaction and high customers loyalty (Gaurav, 2008), cost reduction due to the better understanding of customers needs (Ndubisi, 2004),and expanding use of loyalty marketing programs to build long-term profitable relationships with customers that lead to growth(Ferguson and Hlavinka, 2007) are central to the relationship marketing theory. The application of relationship marketing theory has even extended into financial services, due to the deregulation policy (Yavas and Yasin, 2001), the removal of restrictions between banks, building societies and insurance companies (Speed and Smith, 1992), and the vast expansion in the adoption and use of information technologies (Bergeron et al., 2008). Yet, voices have been raised against overindulgence in IT-based relationship marketing programs as these programs may jeopardize the essence of relationship marketing-i.e. the personal, face-to-face service encounters between providers and clients that are believed to generate client satisfaction(Eisingerich and Bell, 2006). Furthermore, the state of maturity experienced by the banking sector coupled with the inability of the majority of commercial banks to differentiate their offerings have driven banks to pursue relational marketing strategies as opposed to the traditional transactional strategies (Jham and Khan, 2008).This paradigm shift from transactional strategies to relational strategies has obliged the banks to invest in relationship marketing strategies (Claik and Balta, 2006). As far as e-banking is concerned, banks have been keen to investigate the determinants of users’ adoption momentum of e-banking in order to formulate appropriate strategies aimed at meeting the needs and wants of e-banking users and achieving better levels of customer satisfaction and higher loyalty(Poon, 2008).
Therefore, the primary purpose of this paper is to examine the marketing actions (antecedents) affecting relationship quality between Malaysian commercial banks employees and their clients, and the performances (consequences) influenced by relationship quality. It is expected that the higher the bank’s relationship marketing efforts such as client orientation, relational orientation, mutual disclosure, and financial service providers’ attributes, the higher the relationship quality between financial service providers and clients. As the relationship quality increases, it is likely to have a significant influence on the clients’ behavior demonstrated through increased relationship continuity, and word of mouth. However, it is important to note that although the majority of studies attempt to establish a relationship between “higher relationship quality” and” increased relationship continuity” there are other factors that could influence the duration of the relationship. The existence of “behavioural loyalty” or so-called “spurious loyalty is also documented in the financial services literature and as such needs to be addressed too.
This research makes an important contribution to the literature on bank marketing since it is the only study to extend application of relationship quality to the banking context in Malaysia. The current study also contributes to the banking literature as it provides certain managerial implications. The study’s results and recommendations may help management gain a better understanding of factors that contribute to the enhancement of mutually beneficial banking relationship marketing. This may in turn aid in the process of decision –making and strategy formulation.
- مقاله درمورد تاثیر فعالیت های بازاریابی بر کیفیت رابطه در بخش بانکی مالزی
- بررسی فعالیت های بازاریابی موثر بر کیفیت رابطه بین کارکنان بانک های مالزی و مشتریان
- تاثیر فعالیت های بازاریابی بر کیفیت ارتباط در بخش بانکی مالزی
- پروژه دانشجویی تاثیر فعالیت های بازاریابی بر کیفیت رابطه در بخش بانکی مالزی
- تاثیر فعالیت بازاریابی بر رابطه کیفیت در نظام بانکداری مالزی
- پایان نامه در مورد تاثیر فعالیت های بازاریابی بر کیفیت رابطه در بخش بانکی مالزی
- تحقیق درباره تاثیر فعالیت های بازاریابی بر کیفیت رابطه در بخش بانکی مالزی
- مقاله دانشجویی تاثیر فعالیت های بازاریابی بر کیفیت رابطه در بخش بانکی مالزی
- تاثیر فعالیت های بازاریابی بر کیفیت رابطه در بخش بانکی مالزی در قالب پاياننامه
- پروپوزال در مورد تاثیر فعالیت های بازاریابی بر کیفیت رابطه در بخش بانکی مالزی
- گزارش سمینار در مورد تاثیر فعالیت های بازاریابی بر کیفیت رابطه در بخش بانکی مالزی
- گزارش کارورزی درباره تاثیر فعالیت های بازاریابی بر کیفیت رابطه در بخش بانکی مالزی