سنجش شاخص انکساری و شفافیت ناشی از پلاسمون (PIT) در موجبر پلاسمونیک مبتنی بر گرافن


23,500 تومانشناسه فایل: 9475
- حجم فایل ورد: 347.7KB حجم پیدیاف: 368.4KB
- فرمت: فایل Word قابل ویرایش و پرینت (DOCx)
- تعداد صفحات فارسی: 17 انگلیسی: 8
- دانشگاه:
- College of Physics and Electronic Engineering, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, PR China
- College of Modern Education and Technology, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, PR China
- ژورنال: Optics Communications (1)
چکیده
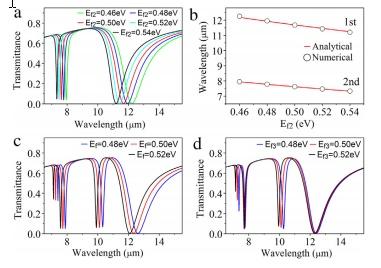
اثر شفافیت ناشی از پلاسمون (PIT) در یک موجبر مبتنی بر گرافن مورد بررسی قرار گرفته است که از یک باس گرافن که با یک نوار گرافن به طور مستقیم جفت شده و با یک حلقه گرافن به طور غیر مستقیم کوپل شده، تشکیل شده است. شبیه سازی های عددی معمول بر اساس روش اجزای محدود (FEM)، برای بررسی خواص گذردهی و بهینه سازی پارامتر های مربوطه استفاده و ثابت شده است که نتایج شبیه سازی با مبانی تئوری آن هم خوانی دارد. سپس به عنوان یکی از کاربرد های بالقوه اثر PIT، خواص حسگری ضریب شکست (شاخص انکساری) با حساسیت بالای 4160 nm/RIU مورد مطالعه قرار می گیرد. این نتایج می تواند در درک اثر PIT و نانو حسگرها کمک کند و همچنین برای مطالعه دستگاه های نانو بر اساس گرافن و کاربردهای آن مفید خواهد بود.
مقدمه مقاله
در سال های اخیر، اثر تداخل کوانتومی یکی از موضوعات داغ در فیزیک تبدیل شده است، چرا که بسیاری از پدیده های فیزیکی مانند شفافیت ایجاد شده به صورت الکترومغناطیسی (EIT) و جذب الکترومغناطیسی (EIA) ، مربوط به اپتیک کوانتومی و فیزیک هسته ای می باشند. EIT از تداخل کوانتومی بین میدان های پالس و پمپ ایجاد می شود که در سیستم های اتمی با سه سطح، رخ میدهد. در مقایسه با EIT ، در سیستم های اتمی، دوگان پلاسمونی EIT یا شفافیت پلاسمونی (PIT) ، بخاطر کاربرد های زیادی که دارد، نظیر حسگرها، کلید های فعال پلاسمونیکی، تبدیل پلاریزاسیون و غیره، توجه زیادی را به خود جلب کرده است. با این حال، بیشتر این ساختارها که در بالا اشاره شد از مواد فلزی تشکیل شده اند و در کاربرد های واقعی اغلب نیاز است که پارامتر های هندسی آن برای کنترل PIT تغییر کند و این موضوع باعث محدود کردن استفاده از فلزات در این ساختار ها شده است. فلز ها همچنین دارای تلفات زیاد و همچنین مشکلاتی اعم از عدم توانایی در کنترل ضریب شکست هستند و بنابراین نمیتوان از آنها به عنوان عناصر فعال برای مدولاسیون استفاده کرد. برای غلبه بر این مشکلات، در سال های اخیر توجهات زیادی بر روی استفاده از گرافن [8-11] برای رسیدن به PIT قابل تنظیم شده است.
گرافن، که یک نوع ماده دوبعدی و دارای کریستال شش گوش از اتم های کربن است، توجه بسیار زیادی را در سال های اخیر بخاطر خواص قابل توجه اپتیکی و الکترونیکی خود جلب کرده است. نتایج جدیدترین تحقیقات نشان میدهد که عملکرد بهبود یافته کلید های با کنترل نوری میتواند در هیبرید مس اکسید شده و گرافن اکسید شده (Cu2O/rGO) بدست آید. گزارش شده است که در لومینسانس نوری قابل تنظیم AGInS گرافن اکسید محلول در آب، دارای کاربرد تصویر برداری در داخل بدن است. در فرکانس های تراهرتز و مادون قرمز میانی ، گرافن میتواند به عنوان یک فلز پلاسمونیکی در نظر گرفته شود. برای تهییج پلاسمون ها در یک موجبر گرافنی، از گرافن با ساختار پریودیک و یا گریتینگ های دی الکتریک زیر طول موج استفاده می شود. در مقایسه با فلز های عادی در رنج فرکانسی مادون قرمز و مرئی، گرافن دارای مزیت هایی از جمله تلفات کم، ظرفیت محدود شدگی مود زیاد و تنظیم پذیر است. محدود شدگی قوی پلاسمون ها در گرافن موجب ایجاد اندرکنش قوی بین نور و ماده میگردد و بنابراین به طور بالقوه میتواند در ادوات اپتیکی به کار گرفته شود. به علاوه، علی رغم فلز های عادی، هدایت سطح گرافن میتواند به راحتی به وسیله دوپ کردن و یا اعمال ولتاژ تغییر کند. با استناد بر این خواص منحصر به فرد، گرافن می تواند جایگزین بسیار مناسب تری برای فلزات در مورد کاربرد های در حوزه جذب کننده، حسگر و PIT باشد.
در جذب پلاسمونی در یک تک لایه گرافن با دو کاواک هوا که با گرافن نانونوار کوپل شده، مورد مطالعه قرار گرفته است. در نویسنده نشان داده است که با قرار دادن تک لایه گرافن زیر گرافنی که به صورت سینوسی خم شده است میتوان به PIT دست یافت. در PIT با چند مورد در یک رزوناتور حلقوی گرافنی مورد مطالعه قرار گرفته است و در [34] یک موجبر چند کاواکه بر پایه گرافن به همراه گذردهی های PIT نشان داده شده است. در، نویسنده به طور تئوری و به وسیله تئوری مد کوپل شده (CMT) مشخصات PIT را نشان داده است که در آن از کوپلینگ های مستقیم و غیر مستقیم استفاده کرده است. اخیرا، وانگ و همکاران ، رزونانس فانو و کاربرد های آن در زمینه حسگری را در یک ساختار بهبود یافته گریتینگ کوپل شده گرافنی را مورد مطالعه قرار داده اند.
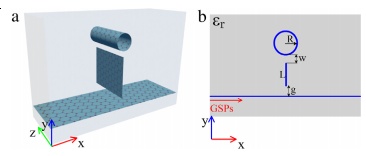
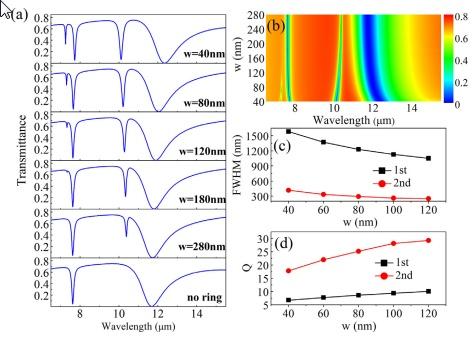
با این حال، تا آنجا که می دانیم، به جز مرجع، چند تحقیقی دیگر در زمینه PIT در موجبر های گرافنی کوپل شده به نوار های رزوناتور گرافن که به صورت عمودی قرار گرفته اند انجام شده است که در آنها نویسنده از دو لایه گرافن با فاصله محدود استفاده کرده است که این لایه ها به صورت متقارن در دو طرف موجبر باس گرافن به عنوان دو رزوناتور جانبی متصل شده برای برای بدست آوردن پدیده های PIT شکل می باشند. گرچه، دو رزوناتور اشاره شده هر دو کاواک های موج استاده(SW) هستند، در حالی که مشخص است که کوپلینگ بین یک موجبر باس و کاواک موج گزرنده (TW) متفاوت هستند. بنابراین با استفاده از خواص منحصر به فرد گرافن و نتایج تحقیقات گزارش شده، این مقاله قصد دارد یک موجبر PIT بر پایه گرافن را بررسی کند که در آن استریپ گرافن که به صورت عمودی قرار داده شده است به عنوان رزوناتور مورد استفاده قرار گرفته است. این استریپ از پایین با یک موجبر باس گرافنی و از بالا با یک حلقه گرافنی کوپل شده است. ضمنا، رزوناتور حلقوی یه عنوان یک کاواک TW عمل می کند در حالی که رزوناتور استریپ به عنوان یک کاواک SW مورد استفاده قرار می گیرد. سپس در این مقاله، اثرات پارامتر های ساختاری و تاثیر پتانسیل شیمیایی گرافن بر روی خواص گذردهی به طور کامل مورد مطالعه قرار گرفته است. علاوه بر این، عملکرد حسگری شاخص انکساری مبتنی بر اثر PIT نیز محاسبه می شود. ساختار پلاسمونیک ارائه شده می تواند راه جدیدی برای خواص PIT در استفاده از کاربرد های دستگاه های فوتونیک مجتمع ایجاد کند.
ABSTRACT Plasmon induced transparency and refractive index sensing in a new type of graphene-based plasmonic waveguide
The plasmon induced transparency (PIT) effect is investigated in a graphene-based waveguide, which is composed of a graphene bus waveguide side-coupled with a graphene strip directly and a graphene ring indirectly. Conventional numerical simulations based on finite element method (FEM) are used to study the transmission properties through optimizing the relevant parameters, and it is proved that the simulation results agree well with the analytical results. Then as one of the potential application branches of the PIT-like effect, the property of refractive index sensing with a higher sensitivity of 4160 nm/RIU is further studied. The result can help to deepen the understanding of PIT-like effect and nano sensor, and it would be also beneficial for the studies and applications of nanoscale graphene-based optical devices.
Introduction
In recent years, the effect of quantum interference has become one of the research hot spots in the field of physics because many physical phenomena are generated in quantum optics and atomic physics, such as electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT) and electromagnetically induced absorption (EIA). The EIT is generated by quantum interference between pumping and probing field, which occurs in three level atomic system [1,2]. Compared with the EIT in atomic systems, the plasmonic analogue of EIT or plasmon induced transparency (PIT) has attracted much attention due to its significant advantages and wide practical applications, such as sensor [3,4], active plasmonic switch [5,6], polarization conversion [7], and so on. However, most of these structures mentioned above are composed of metallic materials and in real application, it is often needed to change their geometrical parameters to realize the dynamic control of the PIT-like window, which significantly limit the scope of their applications. Meanwhile, not only the metallic structures will have larger propagation losses but also it will have difficulties in controlling the permittivity, and it will also result in a lower ability of active modulation. To overcome these shortcomings, many approaches have been focused on the structures using graphene material [8–11] in recent years to achieve dynamic tunability of PIT phenomenon.
Graphene, known as a type of two-dimensional material of which the carbon atoms are packed in honeycomb like crystal lattice [12,13], has attracted particular attention in recent years due to its remarkable electronic and optical properties [14–16]. The latest research results show that enhanced performance of light-controlled conductive switching can be achieved in hybrid cuprous oxide/reduced graphene oxide (Cu2O/rGO) nanocomposites [17]. In [18], tunable photoluminescence of water-soluble AgInZnS-graphene oxide (GO) nanocomposites and their application in-vivo bioimaging are reported. It is well-known that in the mid-infrared and terahertz frequency ranges, graphene can be used as an alternative to the traditional noble-metal plasmonics. To excite the plasmons in graphene-based waveguide, the periodically patterned graphene structures [19], sub-wavelength dielectric gratings [20], have been used in the experiments. Compared with traditional noble metal materials working in visible and near infrared frequencies, graphene has some major advantages [21] such as low loss, extreme mode confinement capacity and dynamic tunability [10,11]. The stronger confinement of plasmons in graphene can create strong light–matter interactions and can be potentially used to build different types of optical devices. Moreover, in contrast to the noble metals, the most notable property of graphene is that its surface conductivity can be flexibly altered by either chemical doping or gate voltage [22–25] without refabricating the structure. Based on these unique characteristics, the graphene has certainly turned to be a very promising material for optical devices analogue to those using noble metals, including absorber [26], sensor [27] and PIT applications [10,28–30].
In [31], plasmon-induced absorption in a single graphene sheet with two air cavities side-coupled to a graphene nanoribbon is investigated. In [32], the authors demonstrated that PIT can be achieved by placing a flat monolayer graphene under a sinusoidally curved graphene layer. In [33], multi-mode PIT in dual graphene ring resonators is studied, and in [34], multicavity-coupled graphene-based waveguide system as well as its PIT transmission is demonstrated. In [35], the authors have theoretically investigated the PIT characteristics using coupled mode theory (CMT) in integrated graphene waveguides with direct and indirect couplings. Recently, Wang et al. investigated the Fano resonance and its sensing application in an improved grating-coupled graphene structure [36].
However, as far as we know, few results have been found for the research of PIT in a graphene-based waveguide coupled to a vertically placed graphene strip resonator except for Ref. [30], where the authors use two graphene sheets with finite length placed symmetrically on both sides of the graphene bus waveguide as two detuned side-coupled resonators to achieve the PIT-like phenomenon. However, the two resonators are both standing-wave (SW) cavity, and it is well-known that the couplings between a bus waveguide and a traveling-wave (TW) cavity or SW cavity are different [35]. Thus inspired by the special properties of graphene and the reported research results, this paper is to design a new type of graphene-based PIT waveguide system, where a vertical placed graphene strip is used as a resonator, and at the same time, it is side-coupled with a graphene ring on the top and with a graphene bus waveguide at the bottom. Meanwhile, the ring resonator works as a TW cavity while the strip resonator works as a SW cavity. Then in this paper, the effects of the structural parameters and chemical potential of the graphene on the transmission characteristics are studied in detail. In addition, the refractive index sensing performance based on the PIT-like effect is also to be calculated. This proposed compact plasmonic structure may pave a new way for the flexible and tunable PIT-like properties in the application of compact integrated photonic devices.

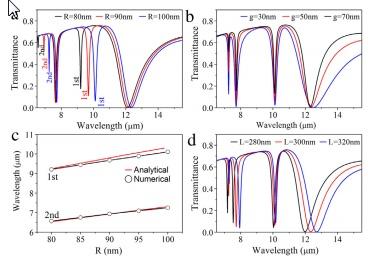
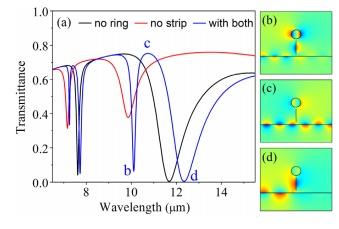
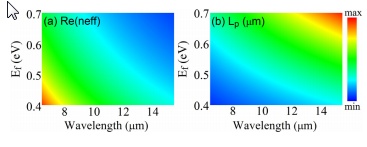
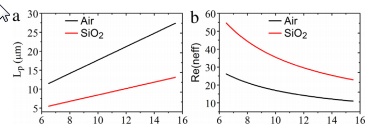
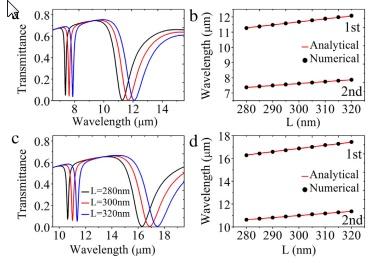
- مقاله درمورد سنجش شاخص انکساری و شفافیت ناشی از پلاسمون (PIT) در موجبر پلاسمونیک مبتنی بر گرافن
- اثر PIT و نانو حسگرها و افزاره های نانو بر اساس گرافن و کاربردهای آن
- شفافیت و شاخص شکست انعقاد ناشی از پلاسما در یک نوع جدید از موجبر پلاسمونیک مبتنی بر گرافن
- پروژه دانشجویی سنجش شاخص انکساری و شفافیت ناشی از پلاسمون (PIT) در موجبر پلاسمونیک مبتنی بر گرافن
- شفافیت و حسگری ضریب انکسار ناشی از پلاسمون در موجبر پلاسمونیک
- پایان نامه در مورد سنجش شاخص انکساری و شفافیت ناشی از پلاسمون (PIT) در موجبر پلاسمونیک مبتنی بر گرافن
- تحقیق درباره سنجش شاخص انکساری و شفافیت ناشی از پلاسمون (PIT) در موجبر پلاسمونیک مبتنی بر گرافن
- مقاله دانشجویی سنجش شاخص انکساری و شفافیت ناشی از پلاسمون (PIT) در موجبر پلاسمونیک مبتنی بر گرافن
- سنجش شاخص انکساری و شفافیت ناشی از پلاسمون (PIT) در موجبر پلاسمونیک مبتنی بر گرافن در قالب پاياننامه
- پروپوزال در مورد سنجش شاخص انکساری و شفافیت ناشی از پلاسمون (PIT) در موجبر پلاسمونیک مبتنی بر گرافن
- گزارش سمینار در مورد سنجش شاخص انکساری و شفافیت ناشی از پلاسمون (PIT) در موجبر پلاسمونیک مبتنی بر گرافن
- گزارش کارورزی درباره سنجش شاخص انکساری و شفافیت ناشی از پلاسمون (PIT) در موجبر پلاسمونیک مبتنی بر گرافن