تاثیر مدل پاسخگویی بار (DR) مسکونی بر تلفات و پروفیل ولتاژ شبکه توزیع برق

22,700 تومانشناسه فایل: 7735
- حجم فایل ورد: 724.3KB حجم پیدیاف: 204.5KB
- فرمت: فایل Word قابل ویرایش و پرینت (DOCx)
- تعداد صفحات فارسی: 20 انگلیسی: 8
- دانشگاه:Lane Department of Computer Science and Electrical Engineering, West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV 26506-6109, United States
- ژورنال: Applied Energy (2)
چکیده
مقاله حاضر، مدلی برای پاسخگویی بار (DR) با استفاده از مدلسازی رفتار مشتری همراه با در نظر گرفتن سناریوهای مختلف و سطوح عقلانیت مختلف را توسعه می دهد. مدلسازی رفتار مشتریان از طریق توسعه ماتریس های الاستیسیته قیمت تقاضا وسیع برای انواع مختلف مشتری ها انجام شده است. از این ماتریس های الاستیسیته قیمت (PEMs) برای محاسبه میزان پاسخگویی بار برای یک مشتری داده شده با توجه به سناریوی قیمت گذاری زمان واقعی روز قبل ، استفاده شده است. مدل های DR به فیدر آزمایشی 8500 گروه IEEE که یک شبکه توزیع شعاعی واقعی بزرگ جهانی است ، اعمال شده است. یک تحلیل جامع در مورد اثرات کاهش تقاضا و توزیع مجدد بر ولتاژها و جریان های سیستم انجام شده است. نتایج حاصل نشان می دهد که DR قابل توجه می تواند ولتاژ سیستم را برای قطع بار بیشتر از طریق تکنیک های مدیریت طرف تقاضا مثل کنترل (VVC) تقویت کند.
مقدمه مقاله
تکامل روند مقررات زدایی در بازار برق منجر به تقسیم سیستم قدرت یکپارچه به حوزه های جداگانه شده است : تولید ، انتقال و توزیع. مقررات زدایی یک رقابت سالم در بازار توزیع در میان شرکت های توزیع ایجاد کرده است. در این فرایند شرکت های توزیع به استراتژی های شبکه هوشمند نوآورانه برای تحقق بخشیدن بهره وری هزینه ، نیاز دارند. بعضی از این ها همانگونه که توسط نیازمندی های شبکه هوشمند شرح داده شده ، به صورت زیر می باشد.
- استقرار و ادغام DR ، منابع طرف تقاضا و منبع بهره وری انرژی
- استقرار تکنولوژی های هوشمند برای اندازه گیری ، ارتباطات مربوط به وضعیت اپراتور شبکه و اتوماسیون تنظیم
- پذیرفتن تکنیک های مدیریت طرف تقاضا (DSM) مثل کنترل Volt/Var، کاهش ولتاژ و غیره
DR و کاهش ولتاژ توزیع رویدادهای مدیریت طرف تقاضای بسیار مهمی هستند که هدف مشترک آنها کاهش تقاضای پیک می باشد. قطع بار پیک موثر توسط اثر ترکیبی کاهش ولتاژ باس ، کاهش تقاضا و توزیع مجدد تقاضا در طول زمان امکان پذیر می باشد. هدف این مقاله ، بررسی نقش احتمالی DR به عنوان یک پارامتر برای کنترل Volt/Var برای بهترین نتایج ممکن کاهش بار برای رسیدن به بهره وری انرژی و سود متقابل برای شبکه و مصرف کنندگان می باشد. DR مسکونی دارای یک پتانسیل برابر با DR صنعتی برای کاهش تراکم در شبکه در طول ساعات پیک می باشد. با این حال ، ایجاد قراردادهای DR با مصرف کنندگان مصنوعی نیاز به مدلسازی مناسب از الگوهای مصرف دارد که در مقایسه با الگوهای مصرف ، مصرف کنندگان صنعتی به مراتب پیچیده تر و تصادفی می باشد. این می تواند توسط نهادهای سرویس دهی بار (LSEs) یا تدوین کنندگان DR (این نهاد ها نیز به عنوان پیمانکاران DR یا به طور ساده تدوین کنندگان نامگذاری شده است) بدست آید. نهادهای سرویس دهی بار می تواند نماینده مصرف کنندگان مصنوعی باشد و قراردادهای DR را با صنایع همگانی برای آن حجم DR که می تواند بدست آید ، امضا کند. برای پیاده سازی موفقیت آمیز چنین قراردادهای DR مسکونی ، نهادهای سرویس دهی بار به مدلهایی جامع DR و بنابراین یک مطالعه الگوهای رفتارِ مصرف کنندگان نیاز دارند. این مقاله برای مدل کردن رفتار مشتری از ماتریس های الاستیسیته تقاضا قیمت استادانه ساخته شده ، استفاده می کند.
بسیاری از کارهای پیشین بر روی توسعه انواع مختلف مدل های DR تمرکز کرده اند. مرجع [2] مقاله قابل توجهی در مورد اصول اساسی در قیمت گذاری لحظه ای برق و تحلیل اقتصادی قیمت گذاری لحظه ای ارائه می کند. همکاری و کمک قابل توجهی در جهت مدلسازی رفتار مصرف کننده به فرم ماتریس های الاستیسیته قیمت (PEMs) در مراجع [3-5] انجام شده است. دیگر مقالات در مجلات پرکاربرد DR ازدید شبکه هوشمند تمرکز کرده اند. یک برنامه زمانبندی تولید با استفاده از توسعه DR برای محاسبه قیمت تسویه بازار زمان واقعی برق در مرجع [6] بسط داده شده است و پخش بار بهینه برای قابلیت اطمینان گرهی یک سیستم با استفاده از کاربرد DR در مرجع [7] انجام شده است. یک مکانیسم مناقصه عمده فروشی شامل ISO ، شرکت برق و مشتری در مرجع [8] پیشنهاد شده است که از مدلسازی مصرف کننده از طریق PEMs استفاده می کند. مدل های بار در مرجع [9] با استفاده از تابع سود مشتری و PEMs توسعه یافته اند و از مدل های نتیجه در یک سیستم واقعی برای نشان دادن نتایج کاهش بار استفاده شده است. همه این مقالات فرض های استانداردی در مورد الاستیسیته قیمت تقاضا راجع به مدلسازی رفتار مشتری کرده اند. با این حال این مفروضات برای یک درک بهتر از الگوهای مصرف برق نیاز به یک پالایش ضروری دارند. کار قابل توجهی بر روی کنترل Volt/Var در مرجع [10] انجام شده است که رهنمودهای اساسی مورد نیاز برای کنترل ولتاژ بهینه در سمت توزیع ولتاژ پایین ارائه می دهد. مرجع [11] یک مفهوم جدید از درنظرگیری DR به عنوان یک پارامتر برای اعمال کنترل Volt/Var بر اساس زمان واقعی برای تحقق بخشیدن به حداکثر پتانسیل هر دو این اندازه گیری های DSM پیشنهاد می کند. در این کار ، PEMs به دقت رفتار مصرف کنندگان مدل توسعه یافته اند. الگوهای DR برای انواع مصرف کنندگان مختلف از این PEMs بدست آمده است و به پخش بار توزیع برای مطالعه ولتاژها و تلفات سیستم یکپارچه شده است. از این گذشته یک مسیر برای هماهنگی DR با کنترل Volt/Var که به نتایج بهتری از قطع بار بویژه در طی ساعات پیک منجر خواهد شد ، کارگذاشته شده است.
این مقاله در 7 قسمت سازماندهی شده است. بخش 2 به طور خلاصه DR و انواع آن را شرح می دهد. بخش 3 یک دید در مورد PEM می دهد و مدلسازی DR با استفاده از PEMs را تشریح می کند. در بخش 4 نمونه اولیه PEM با فرض سطوح عقلانیت مختلف مصرف کنندگان ، توسعه یافته است. بخش 5 به طور خلاصه سیستم توزیع آزمایشی و سناریوهای آزمایشی گوناگون ساخته شده را شرح می دهد . بخش 6 به بحث در مورد آنالیز و تحلیل ولتاژ و تلفات انجام شده بر روی سیستم آزمایشی ، می پردازد . بخش 7 نتیجه گیری می کند و هدف برای کار آینده را ارائه می دهد.
ABSTRACT Residential Demand Response model and impact on voltage profile and losses of an electric distribution network
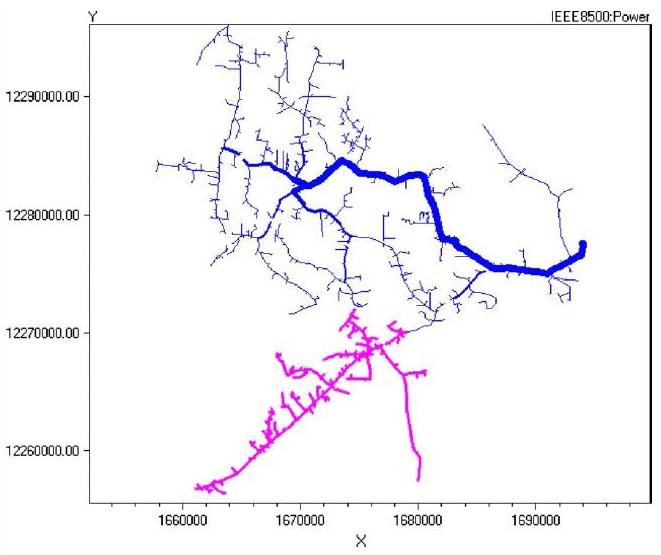
This paper develops a model for Demand Response (DR) by utilizing consumer behavior modeling considering different scenarios and levels of consumer rationality. Consumer behavior modeling has been done by developing extensive demand-price elasticity matrices for different types of consumers. These price elasticity matrices (PEMs) are utilized to calculate the level of Demand Response for a given consumer considering a day-ahead real time pricing scenario. DR models are applied to the IEEE 8500-node test feeder which is a real world large radial distribution network. A comprehensive analysis has been performed on the effects of demand reduction and redistribution on system voltages and losses. Results show that considerable DR can boost in system voltage due for further demand curtailment through demand side management techniques like Volt/Var Control (VVC).
Highlights ► We model electricity consumption patterns of residential consumers using price elasticity matrices. ► Demand Response model is developed for different consumer types from price elasticity matrices. ► Demand Response is integrated into 24 h time series distribution power flow. ► Demand Response boosts system voltage during peak pricing hours providing room for further Volt/Var control. ► Considerable loss reduction resulted during peak hours due to Demand Response
Introduction
The evolution of the deregulation trend in power market has led to the division of integrated power system into individual fields: generation, transmission and distribution. The deregulation has created a healthy competition in the distribution market among distribution companies (Discos). In this process Discos are in need of innovative Smart Grid strategies to realize cost efficiency. Some of these as described by Smart Grid requirements [1] are as follows:
- Deployment and integration of DR, demand side resources and energy efficiency resources.
- Deployment of smart technologies for metering, communications concerning grid operations/status and distribution automation.
- Adoption of Demand Side Management (DSM) techniques like Volt/Var control, voltage reduction, etc.
Both DR and distribution voltage reduction are crucial DSM events that have the common objective of peak demand reduction. Effective peak load shaving is possible by the combined effect of bus voltage reduction, demand reduction and demand re-distribution over time. This paper aims at exploring the possible role of DR as a parameter for Volt/Var Control (VVC) for best possible results of load reduction to achieve energy efficiency and mutual profit for utility and consumers. Residential DR has an equally good potential as industrial DR in mitigating congestion in the network during peak hours. However, establishing DR contracts with residential consumers requires proper modeling of consumption patterns which is far more complicated and random as compared to that of industrial consumers. This could be achieved by load serving entities (LSEs) or DR aggregators (these entities are also being named as DR contractors or simply aggregators). LSEs can represent residential consumers and sign DR contracts with the utility for volume of DR that can be achieved. For the successful implementation of such residential DR contracts, LSEs need comprehensive DR models and thus a study of consumer behavioral patterns. This paper uses elaborate demand-price elasticity matrices (PEMs) to model consumer behavior.
Many previous works have focused on developing different kinds of DR models. Ref. [2] provides substantial literature on fundamental principles on spot pricing of electricity and economic analysis of spot pricing. Significant contribution towards consumer behavior modeling in the form of price elasticity matrices (PEMs) has been done in [3–5]. Other papers in literature are focused on the application of DR from a Smart Grid perspective. A generation scheduling program was developed using elasticity of DR to compute the real time market clearing price of electricity in [6]. Optimal Power Flow for nodal reliability of a system was performed using DR application in [7]. A wholesale bidding mechanism involving ISO, utility and the consumer was proposed in [8] that uses consumer modeling through PEMs. Load models were developed in [9] using customer benefit function and PEMs and the resultant models were used in a real world distribution system to show results of load reduction. All these papers make standard assumptions of demand-price elasticity with respect to consumer behavior modeling. However, these assumptions need vital refinement for a better understanding of electricity consumption patterns. A considerable work has been done on Volt/Var control [10] that provides basic guidelines required for optimal voltage control in the low voltage distribution side. Ref. [11] proposes a novel concept of considering DR as a parameter for applying Volt/Var control on a real time basis to realize the maximum potential of both these DSM measures. In this work, PEMs have been developed to accurately model consumer behavior. DR patterns for different consumer types have been derived from these PEMs and integrated into distribution power flow to study the resulting system voltages and losses. Further, a path has been laid to coordinate DR with Volt/Var control that would yield better results of demand curtailment, especially during peak hours.
This paper is organized into seven sections. Section 2 briefly describes DR and its types. Section 3 gives an insight on PEMs and describes the modeling of DR using PEMs. In Section 4 PEM prototypes have been developed assuming different rationality levels of consumers. Section 5 briefly describes the test distribution system and various test scenarios built. Section 6 discusses the voltage and loss analyses performed on the test system. Section 7 draws conclusions and provides the scope for future work.

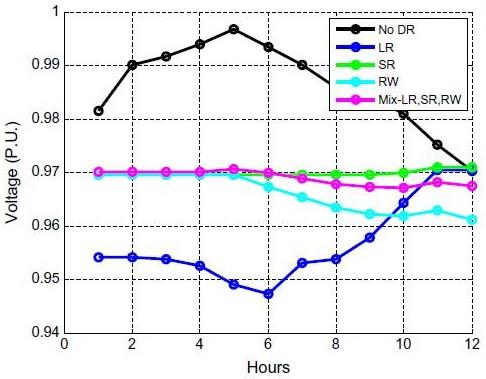
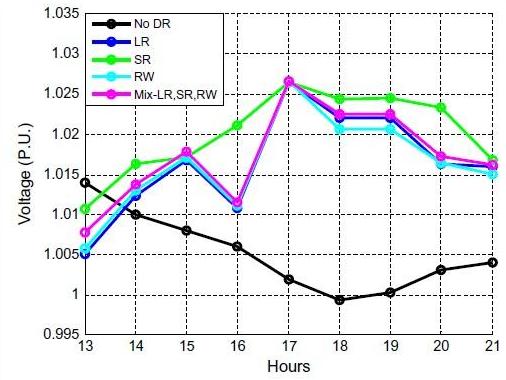
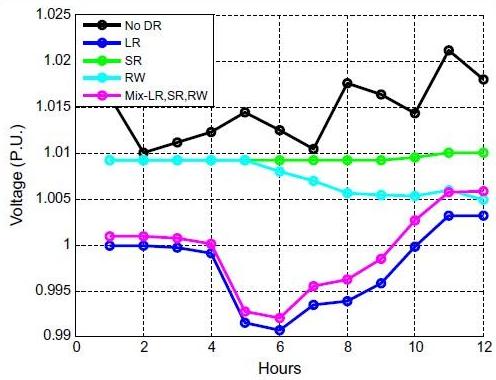
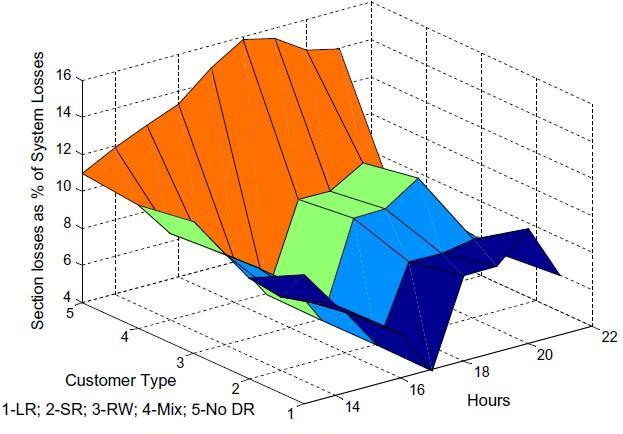
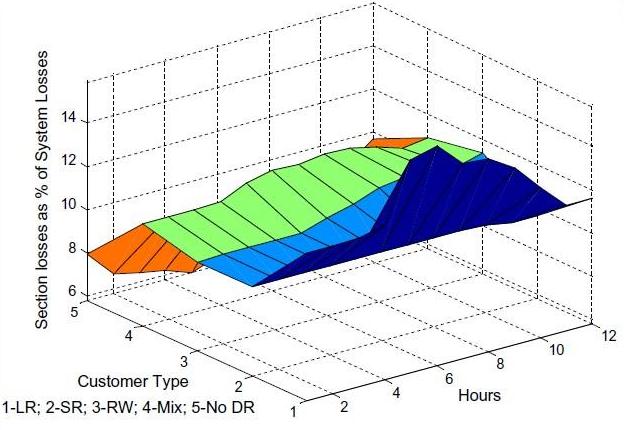
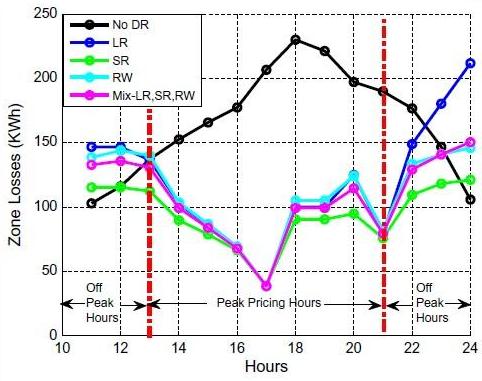
- مقاله درمورد تاثیر مدل پاسخگویی بار (DR) مسکونی بر تلفات و پروفیل ولتاژ شبکه توزیع برق
- مدل پاسخ دهی تقاضای مسکونی و تاثیر مشخصات ولتاژ و تلفات شبکه توزیع برق
- پروژه دانشجویی تاثیر مدل پاسخگویی بار (DR) مسکونی بر تلفات و پروفیل ولتاژ شبکه توزیع برق
- تاثیر مدل پاسخ تقاضای مسکونی بر مشخصات ولتاژ
- پایان نامه در مورد تاثیر مدل پاسخگویی بار (DR) مسکونی بر تلفات و پروفیل ولتاژ شبکه توزیع برق
- تحقیق درباره تاثیر مدل پاسخگویی بار (DR) مسکونی بر تلفات و پروفیل ولتاژ شبکه توزیع برق
- مقاله دانشجویی تاثیر مدل پاسخگویی بار (DR) مسکونی بر تلفات و پروفیل ولتاژ شبکه توزیع برق
- تاثیر مدل پاسخگویی بار (DR) مسکونی بر تلفات و پروفیل ولتاژ شبکه توزیع برق در قالب پاياننامه
- پروپوزال در مورد تاثیر مدل پاسخگویی بار (DR) مسکونی بر تلفات و پروفیل ولتاژ شبکه توزیع برق
- گزارش سمینار در مورد تاثیر مدل پاسخگویی بار (DR) مسکونی بر تلفات و پروفیل ولتاژ شبکه توزیع برق
- گزارش کارورزی درباره تاثیر مدل پاسخگویی بار (DR) مسکونی بر تلفات و پروفیل ولتاژ شبکه توزیع برق