سهم مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری (CRM) ها در توانایی تقسیم بازار


17,400 تومانشناسه فایل: 6747
- حجم فایل ورد: 222KB حجم پیدیاف: 286.4KB
- فرمت: فایل Word قابل ویرایش و پرینت (DOCx)
- تعداد صفحات فارسی: 16 انگلیسی: 10
- دانشگاه:Rey Juan Carlos University, Social Sciences Faculty, Paseo de los Artilleros s/n Madrid 28032, Spain
- ژورنال: Procedia Technology (2)
چکیده
موضوع مطالعه نشان دادن سیستم های مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری (CRM) به عنوان منبعی تکنولوژیکی است، که به درستی اجرا می شود و می تواند با استراتژی تقسیم کارآمد بازار، مهارت های مدیریت را تقویت کند. این تجزیه و تحلیل بر اساس مطالعه موردی گروه VIPs، با توجه به مصاحبه ساختار یافته و با ریاست منطقه مشتری انجام شده است. ما روش های سازمانی را مانند اتخاذ سیستم CRM آن ها، از مراحل اولیه تا انتها و همچنین کاربرد آن ها را توضیح می دهیم. از طریق استفاده از این تکنولوژی، شرکت ها هر دو تهدید و نقاط قوت را به دست می آورند، که در توانایی های دینامیک به کار گرفته می شوند. استفاده هوشمند از این سیستم ها امکان ترکیب منابع مختلف و ایجاد قابلیت های جدید به منظور افزایش مخاطبان هدف، مشتریانی که به محصولات و خدمات شرکت نیاز دارند و تمرکز بر نیازهای آن ها، مورد استفاده قرار می دهند.
مقدمه مقاله
CRM به عنوان یک ابزار تکنولوژیکی در سطح بالایی در سازمان ها قرار دارد. به همین دلیل، اندازه گیری تاثیر آن بر عملکرد مؤسسات امکانپذیر است.
در زمینه جامعه اطلاعاتی که در آن، موانع بین ارتباط و فروش تقریبا قابل مشاهده است، باید در ارتباط با بازار، گرایشات مشتری را دنبال کنیم. به همین علت، پیاده سازی CRM در حال حاضر اغلب در بنگاه ها انجام می گیرد.
یک سازمان بزرگ به سیستم CRM نیاز دارد، دانستن انگیزه های اصلی برای انجام، احتمالات و نتایجی که آنها ارائه میدهند، جالب است. نظریه قابلیت های دینامیک شامل چارچوبی جالب برای تحلیل سهم سیستم CRM در عملکرد موسسات نهایی می شود.
این نظریه اجازه می دهد که نتایج را با دیدگاهی نظری و کاربردی اندازه بگیریم. هدف این نظریه این است که نشان دهد، زمانی که با یک سیستم نوآورانه روبرو می شویم، قابلیت های مؤسسات ارتقا می یابد.
انگیزه اصلی این مقاله نشان دادن نمونه های موفق در عملکرد CRM برای دستیابی به بهترین نتایج است، تا بتوانیم آن را بر نمونه های دیگری که ماهیتی یکسان دارند اعمال کنیم.
CRM (مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری) یا مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری نوعی استراتژی است که از مفهوم هوش تجاری (BI) مشتق می شود. CRM شامل ایجاد رابطه ای نزدیک با مشتریان است و با هدف برطرف کردن نیازهای مشتریان و به دست آوردن اطلاعات مورد نیاز، وفق دادن اولویتهای مشتریان برای دستیابی به عرضه کارآمدتر خدمات در موسسات، انجام می شود. هدف کاربرد آن در مدل های تجاری شامل این موارد می شود: اکتساب، رشد و بهینه سازی نیازهای افراد یا گروه های مشتریان [1].
سازمان ها در هر زمانی به ایجاد بهترین احتمالات تکنولوژی علاقه مند هستند. آن ها در دهه نود ظاهر شدند و به عنوان نیازی برای تطبیق مدیریت و تکنولوژی به منظور ساده کردن فرآیند تجارت انجام می شوند. در این معنا، CRM به استحکام مدل تجارتی مشتری در مرکز آن قرار دارد، کمک می کند. سیستم های برنامه ریزی منابع انسانی (ERP) اجداد CRM هستند، بعضی از اوقات سیستم “دفتر پشتیبانی” خوانده می شود، این نشان می دهد که برعکس سیستم داده های باز، مشتری مستقیماً در این فرآیند شرکت ندارد، در سیستم داده های باز مستقیماً با مشتری ارتباط برقرار می شود (CRM). بنابراین، این مدل از تکنولوژی شامل تکامل مدل های تجاری قبلی می شود.
سازگاری این سیستم در نیروی اطلاعات مرکزی شده است. ارزش آن بر اساس تحلیل داده هایی است که رفتار مشتری را نشان می دهند. با این روش، بهتر می توان به مشتری دست یافت و به آن ها محصولاتی خاص را با روش های پذیرفته شده ارائه کرد؛ که با این روش و با توجه به زمان می توان کارآمدتر بود، و در بازاریابی و روابط مؤسسات نقش مستقیمتری داریم. اصلی ترین مزیت اجرای این سیستم ها، درآمدهایی است که موسسات می توانند با کسب رضایت بیشتر مشتری به دست آورند. این سیستم ها روی کاربران سودآور متمرکز هستند؛ کاربرانی که با استراتژی های وفاداری می توانند سودآورتر باشند و با کاربران جدید تجدید نیرو کنند.
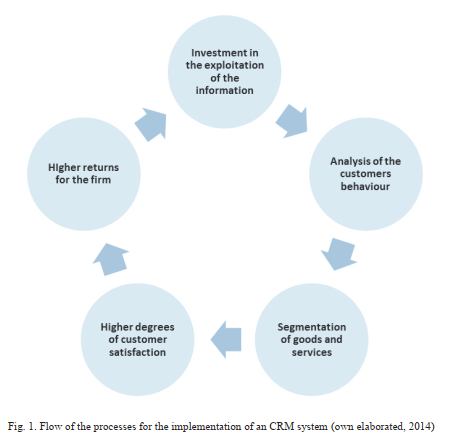
شکل 1: جریان فرآیندهای اجرای سیستم CRM
شکل 1 فرآیندها و اجرای CRM را نشان می دهد. آغاز آن زمانی است که یک شرکت بر استراتژی تجارت خود با مشتری تمرکز کند، و به دنبال ارزش های بالاتر نسبت به آن چیزی است که امروزه محصولات و خدمات از آن برخوردارند.
به این ترتیب، از شرکت، منابع استخراجی و مصرف اطلاعات با توجه به اولویت های مشتری بر اهداف اصلی تقسیم بازار و باز کردن جایگاه های جدید طبق استراتژی های گروهی سفارشی سرمایه گذاری می شود.
ABSTRACT The Contribution of CRMs to the Ability of Market Segmentation: The Case of the VIPS Group
The subject of study is to show CRM (Customer Relationship Management) Systems as technological resources, that properly implemented, can empower the companies’ management skills embodied in an efficient market segmentation strategy. This analysis is based on the case study of VIPs Group, thanks to structured interviews with the head of the Customer’s Area. We explain the organization’s practices as well as the adoption of their CRM system, from early steps to their implementation and use. Through the use of this technology, companies identify both threats and achieved strengths, materialized in dynamic capabilities. The smart use of these systems allows combining different resources in order to provide new capabilities used to increase the target audience, clients who demands company’s products or services, and focusing on their needs.
Introduction
CRM as a technological tool is located at a mature level in Organizations. For this reason, it is possible to measure its impact on firm’s performance.
In the information society context where, the barrier between communication and sales is almost invisible, it is required to follow the customer’s trends in relation to the Market. For this motive, the implementation of the CRM is quite often at firms right now.
As big organizations acquire CRM systems, it is interesting to know the main motives for implementation, possibilities and results that they offer. The theory of dynamic capabilities constitutes an interesting framework to analyze the contribution of CRM systems to final firm’s performance This theory allows measuring the results from a theoretical and practical point of view. It is intended to be demonstrated that when we face a system that allows innovating, firm’s capabilities can be improved. The main motivation for this paper is to show a case of success in CRM implementation oriented to reach best results so that it can be applied to other cases of the same nature.
CRM (Customer Relationship Management) or the management of relationships with customers is a strategy derived from the business intelligence (BI) concept. It consists of establishing a close relationship with customers with the main objective to satisfy their needs and obtain the required information to innovate, adapt their preferences and reach higher degrees of efficiency in the firm’s supply. The objective of its application to the business models consists in the obtaining, development and optimization of individual and group customer needs [1].
Organizations are each time more interested in making the best of these technology possibilities. They appeared in the nineties [2] as a need to align management and technology to simplify business processes. In this sense, it has helped to consolidate the business model centered in customers. Enterprise Resource Planning Systems (ERP) are the ancestors for CRM, occasionally referred as “back office” systems, that indicate that the customer is not directly involved in the process, as opposite to the open data systems (front office), that creates a direct relationship with the consumers (CRM). Therefore, this kind of technology constitutes the evolution of the previous business models.
The adoption of this system is centered on the power of information. Its value is based in the analysis of data that show customer’s behavior. This way, they can better reach the consumers to offer them specific products by means of adapted strategies; that allow being more efficiency in terms of time responses and cost optimization and more direct in the firm’s marketing and communication actions. The main advantage in the implementation of these systems is the returns that firms can have by reaching higher degrees of customer’s satisfaction. It allows being centered on profitable users, whom by means of loyalty strategies can be even more profitable and the recruitment of new users.

Fig. 1. Flow of the processes for the implementation of an CRM system (own elaborated, 2014)
The Figure 1 represents the flow of processes and the implementation of a CRM. It starts when the firm focus its business strategy in the customer, and it demands offer them a higher value than the one obtained in today’s products and services.
This way, from the firm, resources in the exploitation and the consumption of information according to customer’s preferences are invested with the main objective of segmenting the market and open new niches according to group customized strategies.
- مقاله درمورد سهم مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری (CRM) ها در توانایی تقسیم بازار
- مطالعه موردی از گروه VIPS برای مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری (CRM) ها در تقسیم بازار
- سهم CRM ها در توانایی تقسیم بندی بازار: مورد گروه VIPS
- پروژه دانشجویی سهم مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری (CRM) ها در توانایی تقسیم بازار
- سهم CRM ها در توانایی تقسیم بندی بازار
- پایان نامه در مورد سهم مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری (CRM) ها در توانایی تقسیم بازار
- تحقیق درباره سهم مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری (CRM) ها در توانایی تقسیم بازار
- مقاله دانشجویی سهم مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری (CRM) ها در توانایی تقسیم بازار
- سهم مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری (CRM) ها در توانایی تقسیم بازار در قالب پاياننامه
- پروپوزال در مورد سهم مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری (CRM) ها در توانایی تقسیم بازار
- گزارش سمینار در مورد سهم مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری (CRM) ها در توانایی تقسیم بازار
- گزارش کارورزی درباره سهم مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری (CRM) ها در توانایی تقسیم بازار