SFPM: پروتکل تطبیق حفظ حریم شخصی ریزدانه و ایمن جهت شبکه بندی اجتماعی تلفن همراه


24,600 تومانشناسه فایل: 5539
- حجم فایل ورد: 943KB حجم پیدیاف: 849KB
- فرمت: فایل Word قابل ویرایش و پرینت (DOCx)
- تعداد صفحات فارسی: 23 انگلیسی: 8
- دانشگاه:The Information Security and National Computing Grid Laboratory, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu, 610031, China
- ژورنال: Big Data Research (1)
مقدمه مقاله
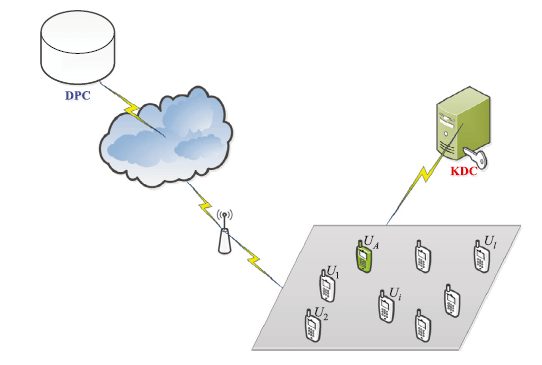
همانگونه از طریق IBM ذکر شد، توسعه سریع شبکهبندی اجتماعی تلفن همراه (MSN) که در شکل 1 نشان داده شده است، تولید کلان دادهها را بهبود بخشید (1). در واقع، آمارهای فراوان حاکی از آن است که اکثر کلاندادههای تولید شده توسط MSN، برای نمونه، گزارشهای دسترسی اینترنت کاربران Unicom در چین به TB 10 در روز رسیده است. به واسطه چنین افزایش موقعیتی، بسیاری از برنامههای مبتنی بر کاوش کلاندادهها و اشتراکگذاری، نظیر سیستمهای پیشنهاد دهنده دوستی WeChat (2) و توییتر (3) و دیگر سیستمهای توصیهکننده شخصی (7-4)، ظهور یافتند. در این برنامهها، هنگام به اشتراکگذاری عمومی اطلاعات شخصی مانند موقعیت و علاقمندیها، افراد میتوانند انواع خدمات مبتنی بر مکان را از سیستمهای توصیهکننده دریافت کنند.
در این مقاله، بر مطالعه نوعی از برنامههای موقعیت محور بسیار محبوب موسوم به پیشنهاد دوستان مجاور (PFR) ذکر شده در (8) تمرکز نمودیم که امکان میدهد کاربران تلفن همراه نزدیک به لحاظ جسمی امکان تعامل رو در روی بیشتری در مکانهای عمومی مانند فرودگاهها، ورزشگاهها و سالنهای قطار داشته باشند (9). به طور کلی، یکی از راههای ممکن استفاده از روش شناخت شده تطبیق مشخصات (10) است که مرحله نخست آن به یافتن کاربر هدف میپردازد.
همانگونه که وو[1] و همکاران به آن اشاره کردند (11)، ماهیت اصلی تطبیق مشخصات آن است دو کاربر به مقایسه ویژگیهای مشخصات شخصی خود پیش از تعامل واقعی نیاز دارند. از این رو، نگرانی دنیای واقعی آن است که ویژگیهای مشخصات اجتماعی مورد استفاده در فرایند تطبیق مشخصات از جمله اطلاعات مهم در مورد کاربران و نقض حریم خصوصی کاربران ویژگیهای اجتماعی میتواند مسائل جدی مطرح کند.
پژوهشهای فعلی حاکی از آن است که فقدان امنیت میتواند کاربران را در معرض تبلیغات ناخواسته (12) و هرزنامهها/کلاهبرداریها، ضررهای اقتصادی یا شهرت اجتماعی قرار دهد (13) و آنها را قربانی باجخواهی یا حتی خشونت فیزیکی میکند (14). از این رو، نگرانیهای مربوط به حریم خصوصی باید هنگام گسترش روشهای انطباق مشخصات در شبکههای اجتماعی تلفن همراه مدنظر قرار گیرد. علاوه بر امنیت، کارفرمایان شبکههای اجتماعی تلفن همراه، ابزارهای تلفن همراه منابع محدود محاسبات را اجرا میکنند. بنابراین، طرح تطبیق ویژگی کارآمدی قدرت و حفظ حریم شخصی برای خدمات اجتماعی تلفن همراه مورد نیاز است.
به تازگی، طرحهای معدودی برای تطبیق مشخصات خصوصی آمده که به دو کاربر امکان مقایسه پروفایلهای شخصیشان را بدون آشکار شدن اطلاعات خصوصی یکدیگر میدهد (15، 10). همانگونه که در (16) ذکر شد، دو روش اصلی برای حل مسئله تطبیق دوستی مبتنی بر ویژگی با حفظ حریم شخصی وجود دارد. نخستین مقوله، به مشخصات فردی به عنوان مجموعهای از ویژگیها توجه داشته و پروتکلهای با طراحی مناسب مبتنی بر فصل مشترک مجموعه خصوصی (PSI) و کاردینالیتی خصوصی مشخصات فردی به عنوان یک بردار در نظر گرفته و مجاورت اجتماعی را با بردار نقطهای یا فاصله برداری نشان میدهد (22-19).
با وجود این، اکثریت قریب به اتفاق رویکردها در مقوله نخست برای فعال نمودن صرفاً تطبیق خصوصی درشتدانه ارائه شده و به کاربران با ویژگی (ها) یکسان که در برنامههای کاربردی کمتر عملی میباشد، چنین امکانی نمیدهد (23). برای حل این مسئله و بنابراین بهبود بیشتر قابلیت استفاده PFR در MSN، تطبیق خصوصی ریز دانه به صورت گسترده ای در مقوله دوم استفاده شده که ایده اصلی پژوهش این مقاله محسوب میشود. از این رو، در ادامه به بحث در مورد آثار مرتبط با مقوله دوم میپردازیم.

لیانگ[2] و همکاران، روش مستعارهای متعددی را برای بهبود حفاظت از ناشناخته ماندن پروتکل تطبیق مشخصات در (19) پیشنهاد نمودهاند، که در آن محاسبه ضرب نقطهای یکی از مهمترین اساس آن محسوب میشود. از دیدگاه انعطافپذیری، روش مستعارهای متعدد میتواند ناشناس بودن را تضمین کند، اما نمیتواند انعطافپذیری با تعداد کمی بیشتر از مستعارها را که در آن به فضای زیاد و مدیریت بالاسری نیاز است را برآورده نماید.
در (21)، ژانگ و همکاران پروتکل تطبیق خصوصی ریزدانه ای را با سطوح مختلف حریم خصوصی در شبکههای اجتماعی تلفن همراه مجاورت محور طراحی کردند که معیارهای تطبیقی متفاوتی را در برداشت: l1 فاصله و حداکثر فاصله. با وجود این، توجه به تفاوت آیتمهای مشخصات حائز اهمیت نیست و قادر به افتراق کاربران با مقدار فاصله l1 یا حداکثر فاصله نیست.
او و همکارانش (24) این موضوع را با ارائه پروتکل تطبیق مشخصات کاربر جدید با قابلیت خودکنترلی مورد توجه قرار داده که در آن به کاربران امکان خود تعریفی آیتمهای وزندهی شده پروفایل در طول تطبیق وجود دارد و بنابراین، نتایج تطبیقی دقیقتری برای کاربران فراهم میآورد. متاسفانه، روش تطبیق اطلاعات همسان در (21) و (24) هر دو بر رمزگذاری زمانبری (25) مبتنی است که همگنی را برآورده مینماید.
بنابراین، به واسطه هزینههای سنگین رمزگذاری و کشف رمز، بهبود عملیات کلی برنامههای MSN دشوار است. هدف این مقاله، حفظ آیتمهای مشخصات خصوصی از افشا و در عین حال بهبود کارآیی برنامههای مقولههای دوم است. به منظور بهبود اثربخشی، ما از برخی روشهای کارآمد برای محاسبه ایمن محصول ضرب نقطهای استفاده میکنیم و این در حالی است که روشهای کارآمد اساساً بر دو نوع وجود دارند. یکی از رمزگذاریهای نامتقارن جدید حفظ محصول اسکالر از سوی وانگ[3] و همکاران پیشنهاد شده است (22)، که بر مسئله محاسبه همسایگی نزدیکترین k (kNN) در پایگاه داده رمزگذاری شده متمرکز است و از این رو نمیتواند انعطافپذیری با تغییرات آیتمهای ویژگی را برآورده نماید.
مورد دیگر محاسبه شباهت (PPCS) کسینوسی حفظ حریم شخصی کارآمد مطرح شده از سوی لو و همکاران (26) میتواند به عنوان مبنای بسیاری از زمینههای پژوهشی مانند کاوش کلان داده حفظ حریم شخصی، کنترل دسترسی داده و سیستم توصیه به کار گرفته شود. نتایج شبیهسازی گسترده نشان داده است که پروتکل PPCSC ، از نظر سربارهای ارتباطی و محاسبه یکی از کارآمدترینها تلقی میشود. بنابراین، پروتکل PPCSC را به عنوان مبنای پروتکل خود انتخاب کردیم.
علاوه بر این، اکثر پروتکلهای انطباق مشخصات با حفظ حریم شخصی، الگوی حمله را مدنظر قرار نداده است. برای درک بهتر، هیچ یک از راه حلهای فعلی برای تطبیق مشخصات همه ویژگیهای مطلوب را ندارند: حفظ حریم شخصی، امنیت (برای نمونه، احراز هویت و سازماندهی)، راندمان (برای نمونه، بالاسری ارتباطی و محاسبه کارآمد هزینه) و انعطافپذیری.
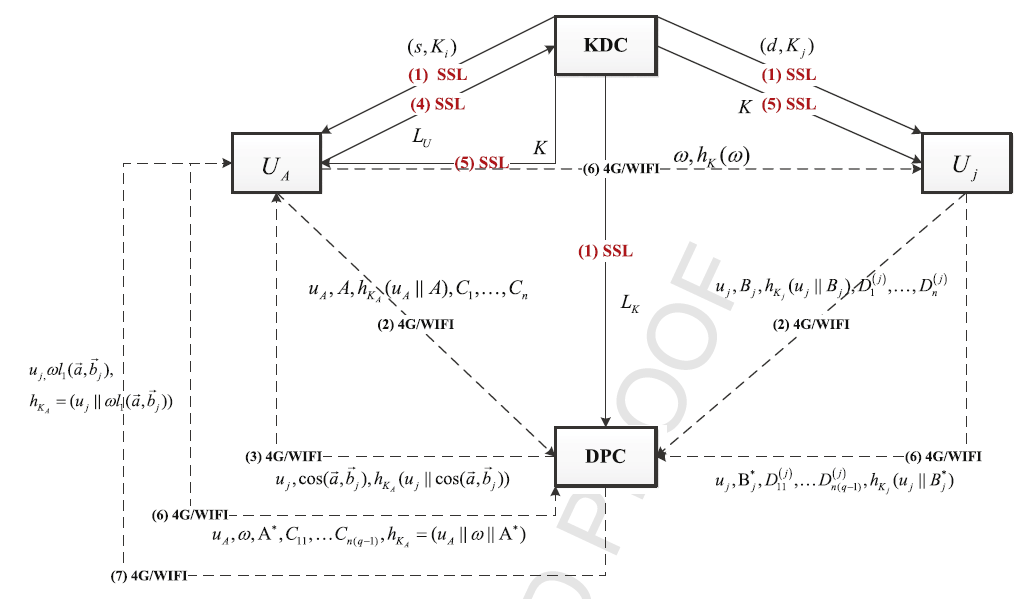
بنابراین، چگونگی دستیابی به پروتکل انطباقی مشخصات با حفظ حریم شخصی و به صورتی کارآمد و انعطافپذیر کماکان چالشی در MSN مجاورت محور محسوب میشود. نظر به چالش فوق، در این مقاله پروتکل تطبیقی با حفظ مشخصات فنی و ریز دانه و ایمن موسوم به SFPM را برای MSN مبتنی بر مجاورت معرفی میکنیم. با پروتکل SFPM، کاربران میتوانند به صورت کارآمد و انعطافپذیر به دنبال هدف تطبیق ریزدانه بدون افشای هیچ یک از اطلاعات شخصی باشند. علاوه بر این، پروتکل پیشنهادی ما به یکپارچگی پیام و اعتبار منبع داده دست مییابد و به صورت فوقالعادهای هزینه محاسبه در مقایسه با پروتکل پیشنهاد شده در (21) و (24) کاهش مییابد، به ویژه بار محاسباتی و محاسباتی بر گوشیهای هوشمند کاهش مییابد. به طور خاص، هدف اصلی این مقاله بر چهار جنبه است:
- ما SFPM یعنی پروتکل تطبیق حفظ حریم شخصی ریزدانه و ایمن جدید را ارائه کردیم که مشتمل بر دو مرحله تطبیق است: کسینوس شباهت و معیار l1 وزندهی شده. با SFPM، کاربران میتوانند کاربران را به صورت ریزدانه تشخیص داده و منطبقترین مورد را با آن بیابند.
- در مقایسه با پروتکلهای انطباقی خصوصی پیشین، SFPM سبک تطبیقی کارآمد و انعطافپذیر ارائه میکند. به طور خاص، ما مرکز پردازش داده (DPC) را برای انجام محاسبات انطباقی معرفی میکنیم که میتواند به طرز چشمگیری بار محاسباتی و ارتباطی ابزارهای تلفن همراه را بهبود بخشد. علاوه بر این، الگوریتم کدگذاری پیشنهاد شده در (26) در مقایسه با (22) کارآمدتر و انعطافپذیرتر است. این مسئله را زمانی که کاربر به برخی ویژگیها علاقمند است یعنی صرفاٌ ویژگیهای درج شده باید گذاری شود و در نتیجه DPC صرفاً افزایش رو بر این ویژگیها اجرا میکند و آنها را به نتایج محاسباتی پیشین میافزاید، در نظر بگیرید. حذف و بروزرسانی عملیات با درج مشابهت دارد. بنابراین، پروتکل ما برای تایید ویژگیهای فردی انعطافپذیر است.
- علاوه بر محرمانه بودن اطلاعات، پروتکل SFPM یکپارچگی پیام و اعتبار منبع داده را با افزودن کد تایید هویت پیام نظیر اثرانگشت برای کد احراز هویت پیام (HMAC) دریافت میکند و در نتیجه، متن پیام رمز میتواند از نویزهای افزایشی دفاع کند.
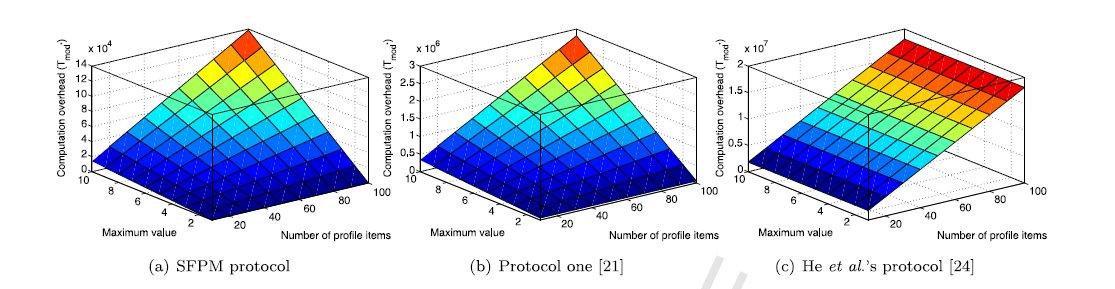
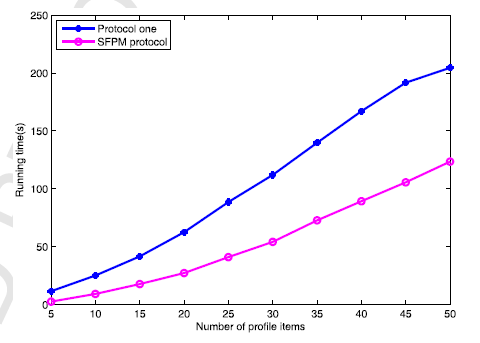
- برای اعتباربخشی به کارآیی پروتکل SFPM پیشنهادی، پروتکل SFPM و پروتکل پیشنهاد شده توسط ژانگ (21) را بر بستری با دو تلفن اندرویدی و یک کامپیوتر اجرا کردیم. ما میتوانیم تعیین کنیم که SFPM از نظر هزینه محاسباتی، کارآمدتر از طرحهای تطبیق مشخصات مشابه موجود (24، 21) است.
ادامه این مقاله بدین صورت سازماندهی شده است. در بخش 2، الگوی سیستمی را رسمی نموده و هدف طراحی را تایید میکنیم. پس از آن، پروتکل SFPM را در بخش 3 تشریح میکنیم. تحلیل امنیت و ارزیابی عملکرد در بخشهای 4 و 5 آمده است. در نهایت، در بخش 6 به نتایج اشاره میکنیم.
[1] Wu
[2] Liang
[3] Wong
ABSTRACT SFPM: A Secure and Fine-Grained Privacy-Preserving Matching Protocol for Mobile Social Networking
In emerging big data era, mobile social networking (MSN) is an important data source, which provides an attractive proximity-based communication platform for mobile users with similar interests, attributes, or background to communicate with each other. In this kind of proximity-based MSN, profile matching protocol, which enables a mobile user to break the ice and start a conversation with someone attractive, is one of important components for its success. However, profile matching may occasionally leak the sensitive information, hence privacy concerns often hinder users from enabling this functionality. Aiming at this problem, in this paper, we present a new secure and fine-grained privacy-preserving matching protocol, called SFPM. Differently from those previously reported private profile matching schemes, our proposed SFPM can fine-grainedly differentiate users with the same value of matching metrics by two phases of profile matching. In addition to the personal privacy preservation through secure and efficient cryptographic algorithm, SFPM also achieves the flexibility of profiles changing at the same time. Extensive performance evaluations via smartphones with android system are conducted, and experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the SFPM protocol.
Introduction
As mentioned by IBM, the rapid development of mobile social networking (MSN) shown in Fig. 1, promotes the generation of big data [1]. Actually, plentiful statistics have indicated that most of big data are produced by MSN, for example, the internet access records of Unicom users have reached 10 TB each day in China. Because of this rising situation, many applications based on big data mining and sharing, like the friend recommender systems of WeChat [2] and Twitter [3], and other personalized recommender systems [4–7], have been emerged. In these applications, when sharing the personal information, like location and preferences in public, people can receive a variety of useful location-based services from these recommender systems. In this paper, we focus on studying a kind of very popular location-based applications, called proximity-based friend recommendation (PFR) mentioned in [8], which allows physically proximate mobile users to have more tangible face-to-face social interaction in public places such as airports, trains and stadiums [9]. In general, one possible way is to use the widely known profile matching [10] technique, which is the first step to find the targeting user. As stated by Wu et al. [11], the essence of profile matching is that two users need to compare their personal profile attributes before real interaction. However, a real-world concern is that social profile attributes used in the profile matching process include sensitive information about users and the violation of the privacy of the users’ social profiles may pose serious problems. Existing researches show that loss of privacy can expose users to unwanted advertisements [12] and spams/scams, cause social reputation or economic damage [13], and make them victims of blackmail or even physical violence [14]. Hence, the privacy concerns must be addressed when developing profile matching techniques for mobile social networks. In addition to security, clients of mobile social networks run on computing resource-constrained mobile devices. Therefore, a privacypreserving and power-efficient profile matching scheme is needed for mobile social services. Recently, there are quite a few schemes for private profile matching, which allow two users to compare their personal profiles without revealing private information to each other [10,15] have been researched. As mentioned in [16], there are two main streams of approaches to solve the privacy-preserving profile-based friend matching problem.

The first category treats the personal profile as a set of attributes and provides well-designed protocols based on private set intersection (PSI) and private cardinality of set intersection (PCSI) [10,17,18]; The second category considers the personal profile as a vector and measures the social proximity by private vector dot product or vector distance [19–22]. However, the vast majority of approaches in the first category have been proposed to enable only coarse-grained private matching and are unable to further differentiate users with the same attribute(s), which is less practical in applications [23]. To solve this problem and thus further enhance the usability of PFR in MSN, fine-grained private matching have been widely used in the second category, which are the basic idea of research in this paper. Hence, in what follows, we mainly discuss some related works of the second category.
Liang et al. proposed the multiple pseudonyms technique to improve the anonymity protection for profile matching protocol in [19], where secure dot-product computation is one of important building block. From the perspective of flexibility, multiple pseudonyms technique can ensure anonymity, but, it cannot satisfy the flexibility with slightly larger number of pseudonyms, which actually requires a lot of storage space and management overhead. In [21], Zhang et al. designed a fine-grained private matching protocol with different privacy levels in proximity-based mobile social networks, which included different matching metrics: l1 distance and max distance. However, it did not consider the difference of profile items and is unable to further differentiate users with the same value of l1 distance or the max distance. He et al. [24] addressed this issue by proposing a novel user self-controllable profile matching protocol, which allowed users to self-define the weighted of profile items during matching, thus provided more accurate matching results for users. Unfortunately, the method of matching information similarity in both [21] and [24] was based on the time-consuming paillier encryption [25] satisfying homogeneity. Thus, due to the heavy overheads of encryption and decryption, it is difficult to improve the overall operating of MSN applications. The purpose of this paper is to preserve private profile items from disclosing while improving the efficiency of schemes of the second category. In order to improve efficiency, we utilize some efficient methods to securely compute the vector dot product, while existing efficient methods are mainly two kinds. One is a new asymmetric scalar-product-preserving encryption proposed by Wong et al. [22], which is focused on the problem of k-nearest neighbor (kNN) computation on an encrypted database, however, it cannot satisfy the flexibility with the variation of profile items. The other is an efficient privacy-preserving cosine similarity computing (PPCSC) protocol proposed by Lu et al. [26], which could serve as the foundation of many research fields, like privacy-preserving big data miming, data access control, recommendation system. Extensive simulation results showed that the PPCSC protocol is the most efficient one in terms of computation and communication overheads. Thus, we choose the PPCSC protocol as the basis of our protocol. Moreover, most of privacy preserving profile matching protocols do not consider the attack model. To the best of our knowledge, none of the existing solutions to profile matching possesses all the desired properties: privacy-preserving, security (e.g., authentication and integrity), efficiency (e.g., cost-effective computation and communication overhead) and flexibility.
Therefore, how to achieve an efficient, flexible and privacypreserving profile matching protocol is still challenging in proximity-based MSN. Aiming at the above challenge, in this paper, we propose a secure and finer-grained privacy-preserving matching protocol, called SFPM, for proximity-based MSN. With the SFPM protocol, users can efficiently and flexibly seek out the finergrained matching target while without disclosing any personal information. In addition, our proposed protocol achieves the integrity of the message and source data authentication, and immensely decreases the computation overhead in comparison with that proposed in [21] and [24], especially alleviating the computational and communication burden of smartphones. Specifically, the main contributions of this paper are four aspects.
- We present SFPM, a new secure and fine-grained privacypreserving matching protocol, which consists of two stages matching: cosine similarity and weighted l1 norm. With SFPM, users can finer-grainedly distinguish users and find out the most matched one.
- Compared to the previous private matching protocols, SFPM provides a flexible and efficient matching style. In particular, we introduce a data processing center (DPC) to accomplish matching computations, which can immensely relieve the computation and communication burden of mobile devices. Moreover, the encryption algorithm proposed in [26] is more efficient and flexible compared with [22]. Consider the case when user inserts some profiles, only the inserted profiles should be encrypted, and then DPC only executes multiplication on these profiles and adds them in the previous computation result. Deleting and updating operations are similar with inserting. Therefore, our protocol is flexible for the variation of personal profiles.
- In addition to data confidentiality, the SFPM protocol achieves the integrity of the message and source data authentication by appending the message authentication codes, like the keyedhashing for message authentication code (HMAC), as a result
- To validate the effectiveness of the proposed SFPM protocol, we implement both the SFPM protocol and the protocol one proposed by Zhang [21] on a platform with two android phones and a computer. By contrasting, we demonstrate that SFPM is much more efficient than existing similar profile matching schemes [21,24] in terms of the computational overhead.
the ciphertexts can defense the additive noise.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. In Section 2, we formalize the system model and confirm the design goal. After that, we propose the SFPM protocol in Section 3. The security analysis and performance evaluation are introduced in Section 4 and 5, respectively. Finally, we draw our conclusions in Section 6.
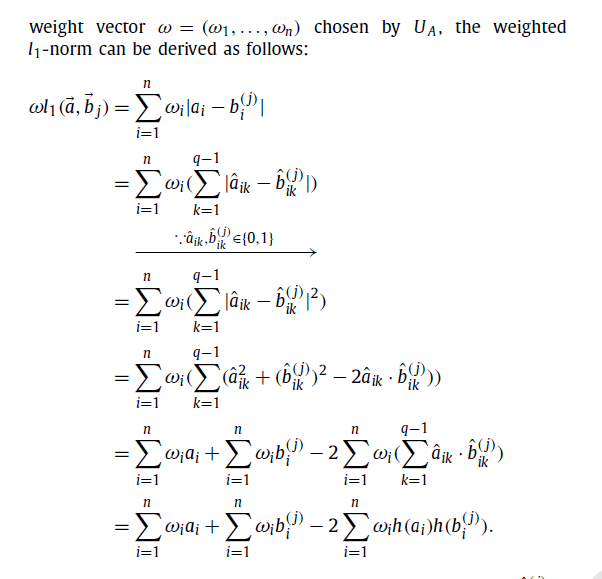
- مقاله درمورد SFPM: پروتکل تطبیق حفظ حریم شخصی ریزدانه و ایمن جهت شبکه بندی اجتماعی تلفن همراه
- شبکه بندی اجتماعی تلفن همراه با SFPM : پروتکل تطبیقی ریزدانه و ایمن با حفظ حریم فردی
- پروژه دانشجویی SFPM: پروتکل تطبیق حفظ حریم شخصی ریزدانه و ایمن جهت شبکه بندی اجتماعی تلفن همراه
- SFPM به عنوان پروتکل تطبیقی جهت شبکه بندی اجتماعی تلفن همراه
- پایان نامه در مورد SFPM: پروتکل تطبیق حفظ حریم شخصی ریزدانه و ایمن جهت شبکه بندی اجتماعی تلفن همراه
- تحقیق درباره SFPM: پروتکل تطبیق حفظ حریم شخصی ریزدانه و ایمن جهت شبکه بندی اجتماعی تلفن همراه
- مقاله دانشجویی SFPM: پروتکل تطبیق حفظ حریم شخصی ریزدانه و ایمن جهت شبکه بندی اجتماعی تلفن همراه
- SFPM: پروتکل تطبیق حفظ حریم شخصی ریزدانه و ایمن جهت شبکه بندی اجتماعی تلفن همراه در قالب پاياننامه
- پروپوزال در مورد SFPM: پروتکل تطبیق حفظ حریم شخصی ریزدانه و ایمن جهت شبکه بندی اجتماعی تلفن همراه
- گزارش سمینار در مورد SFPM: پروتکل تطبیق حفظ حریم شخصی ریزدانه و ایمن جهت شبکه بندی اجتماعی تلفن همراه
- گزارش کارورزی درباره SFPM: پروتکل تطبیق حفظ حریم شخصی ریزدانه و ایمن جهت شبکه بندی اجتماعی تلفن همراه