کاربرد فیلتر توان فعال سری هیبرید (HSAPF) قوی در بهبود کیفیت توان


شاپا پرینت: 0885-8993 وبسایت مرجع 15 رفرنس دارد
25,800 تومانشناسه فایل: 9310
- حجم فایل ورد: 725KB حجم پیدیاف: 1MB
- فرمت: فایل Word قابل ویرایش و پرینت (DOCx)
- تعداد صفحات فارسی: 23 انگلیسی: 10
- دانشگاه:Department of Electrical Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Rourkela-769 008, India
- ژورنال: IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics (1)
چکیده
کاهش کیفیت توان سبب اثرات اقتصادی جانبی روی مشتریان و خدمات میشود. هارمونیکهای جریان و ولتاژ یکی از رایج ترین موضوعات کیفیت توان هستند که توسط فیلتر توان فعال سری هیبرید (HSAPF) حل شدهاند. در این مقاله، طراحی یک کنترلر جدید با استفاده از کنترلر مود-2 کشویی [sliding] برای ایجاد HSAPF سختتر و پایدارتر ارائه شده است. یک مدل دقیقتر متوسط HSAPF سه فاز از این مقاله بدست آمده است. مفهوم طراحی HSAPF قوی از طریق مطالعات تجربی و شبیه سازی مورد بررسی قرار گرفتهاند و نتایج بدست آمده مورد بحث قرار گرفتهاند.
مقدمه مقاله
در طول چند سال گذشته، افزایش شدید استفاده از خطوط غیرخطی، باعث بوجود آمدن موضوعات کیفیتی توانِ اضافی از جمله هارمونیکهای جریان بالا، اعوجاج ولتاژ، عامل ضریب توان و غیره در شبکههای برق شده است. از اینرو بار غیرخطی در سیستم، جریانهای هارمونیکی ایجاد میکند و آنها را به خطوط توان AC تزریق میکند. این جریان و ولتاژ تغذیه اعوجاجی باعث خرابی برخی قطعات حفاظتی، سوختن ترانسفورماتورها و موتورها، و گرمای بیش از حد کانال میشود. بنابراین، نصب دستگاههای جبرانساز برای جبران جریانهای هارمونیک و ولتاژهای تولید شده ناشی از بار غیرخطی خیلی مهم میباشد. به طور سنتی، فیلترهای توان پسیو به عنوان یک قطعه جبرانساز مورد استفاده قرار گرفتند تا اعوجاج ایجاد شده توسط بارهای غیرخطی ثابت را جبران کنند. این فیلترها[2] برای ارائه یک مسیر امپدانسی کوتاه برای هارمونیکها و حفظ کیفیت توان خوب با یک طراحی ساده و قیمت پایین طراحی شدهاند. با اینحال، فیلترهای پسیو معایبی مثل تنظیم اشتباه، رزونانس، وابستگی در شرایط سیستم تغذیه توان و مقادیر بزرگ مؤلفههای پسیو دارند که منجر به پیاده سازی های بزرگ میشود.
در زمانی که توان با کیفیت بالا نیاز است، توپولوژیهای فیلترهای فعال مثل APF بصورت سری یا موازی (فیلترهای اکتیو سری و فیلترهای اکتیو موازی) به بارهای غیرخطی وصل میشوند تا باعث بهبود اعوجاج ولتاژ یا جریان شوند. این فیلترها راه حلهای گستردهای هستند، و به عنوان از بین برنده اعوجاج جریان مؤثر و توان راکتیو تولید شده توسط بارهای غیر خطی بکار میرود[3]و [4]. این توپولوژی، توجه بیشتری برای تحمل جریانهای بار بالا جذب میکند و به عنوان یک ایزولاتور و جداکننده بین منبع و بار غیرخطی عمل میکند. این استراتژی کنترل برای بهبود HSAPF مهم میباشد. در واقع، مقالات بسیاری برای فیلتر توان هیبرید تکنولوژیهای پیشرفته ارائه شدهاند که باعث کاهش هارمونیکهای جریان ایجاد شده توسط این با های غیرخطی میشوند. اما این کنترلر برای عملکرد هر دو حالت پایدار و گذرا با استراتژی کنترل خطی آسان نیست چون مدل دینامیکی سیستم HSAPF شامل ضرب ورودیهای کنترل و متغیرهای حالت میباشد. باتوجه به ویزگی های غیرخطیHSAPF، یک کنترلر مد لغزشی در [8] ارائه شده است. کنترل مد لغزشی با عنوان یک روش کنترل مناسب برای کنترل سیستم غیرخطی با دینامیک نامشخص و اختلالات به دلیل ویژگی کاهش و حساسیت کم به اختلالات و تغییرات پارامترشناخته شده میباشد، که بار مورد نیاز مدلسازی دقیق را کاهش میدهد. علاوه براین، این کنترل مدل لغزشی پیچیدگی طراحی کنترل فیدبک را با استفاده از جدایی سیستم به دو زیرسیستم مستقل با ابعاد کوچکتر، کاهش میدهد. به دلیل این خصوصیات داده شده، اجرای کنترل مد لغزشی در مناطق قطعات سوئیچینگ الکترونیکی توان یافت میشوند. اصل کنترل مد لغزشی تعریف شده تا حرکت مد لغزشی در یک سطح سوئیچینگ از پیش تعیین شده در فضای حالت سیستم با استفاده از کنترل ناپیوسته اجرا شود. سطح سوئیپچینگ بایدبصورتی انتخاب شود که حرکت لغزشی دینامیک مورد نظر حرکت را با توجه به معیارهای عملکرد مناسب حفظ کند. روشهای کنترل معمولی، مثل تنطیم کننده خط درجه دوم(LQR) [9] یا کنترلر سروو گوسی درجه دوم(LQG) [10] در سیستمهای خطی باید سطوح سوئیچینگ مناسب انتخاب کنند. سپس، کنترل ناپیوسته باید طوری انتخاب شود که هر خروجی حالت سطح ناپیوستگی به سطح زمانِ محدود برسد. براین اساس، مد لغزشی در امتداد سطح رخ میدهد و سیستم دینامیک سیستم مورد نظر را دنبال میکند.
مشکل اصلی پیاده سازی سخت افزاری مدل کنترل مد لغزشی کلاسیک ناشمرده بودن[chattering] آن است. ناشمرده بودن چیزی نیست اما یک پدیده نامطلوب نوسانی با دامنه و فرکانس است. ناشمرده بودن خطرناک است چون سیستم از دقت سیستم، پوشش حرکتی قسمتهای مکانیکی عقب میماند و تلفات گرمایی بالا در مدارهای توان الکتریکی رخ میدهد. ناشمرده بودن به دلیل دینامیکهای مدل نشده رخ میدهد. این دینامیکهای مدلسازی نشده از مکانیزم سرو، سنسورها و پردازنده اطلاعات با ثابت زمانی کوچکتر ایجاد شدهاند. در کنترل مد لغزشی فرکانس سوئیچینگ با به مقدار قابل توجهی زیاد باشد تا کنترلر را قوی و ثابت کند و ناشمرده بودن نباید وجود داشته باشد و اگر فرکانس سیستم افزایش یابد، ناشمرده بودن کاهش مییابد. استفاده از کنترلر مد لغزشی در سیستمهای مبدل توان مثل HSAPF، یک راه طبیعی برای کاهش ناشمرده بودن است و فرکانس سوئیچینگ را افزایش میدهد. با اینحال، این در مبدلهای توان بخاطر محدودیتهای خاص در فرکانس سوئیچینگ در تلفات در مبدلهای توان امکانپذیر نیست، و در ناشمرده بودن تأثیر میگذارد. بنابراین، مشکل ناشمرده بودن نمیتواند اجرای مد لغزشی را مقصر بداند چون بصورت عمده توسط محدودیتهای سوئیچینگ رخ میدهد. در [11]، نشان داده شده که اگر درجه نسبی سیستم با دیسک یا سنسورها برابر دو باشد، ناشمرده بودن بصورت نمایی متمایل به صفر است. درجه نسبی سیستم HSAPF دو است. بخاطر این درجه نسبی سیستم HSAPF و همچنین بخاطر این موانع در کنترلر مد لغزشی کلاسیک، این مقاله یک کنترلر جدید مثل کنترلر-2 مد لغزشی ارائه میکند. کنترلر ارئه شده ناشمرده بودن را سرکوب میکند و عملکرد HSAPF رابهبود میبخشد. این کنترلر برای این توپولوژی HSAPF کاملاً جدید است. مقالات اخیر[12] بر روی حامل مبتنی بر PWM (CBPWM) برای توپولوژی HSAPF تمرکز میکند. اما در بعضی حالات CBPWM مبتنی بر HSAPF ممکن است کاملاً در بیشتر شرایط دنیای واقعی قابل اندازه گیری نباشد. در حالت CBPWM، انحراف سیستم توان در نظر گرفته نمیشود و همچنین وجود یک تأخیر زمانی در نقطه ردیابی [tracking] مرجع به پاسخ کوتاه سیستم کلی افزایش مییابد. بنابراین، خطای ردیابی به طور موثری کاهش نمییابد و پایداری سیستم حداقل افزایش مییابد. برای غلبه بر این، یک کنترلرSMC-2 برای مبدل منبع ولتاژ(VSC) ارائه شده است. ایده کنار این کنترلر برای رسیدن به افزایش پایداری، ردیابی کامل و اعوجاج جریان آزاد و ولتاژ بار میباشد. با در نظر گرفتن مسائل بالا، تاکید بیشتری بر روی توسعه کنترلر قوی با یک رویکزد ردیابی مرجع سریعتر در HSAPF میکنیم، که به همه اختلالات مثل اختلال ولتاژبار، تغییرات پارامتری بار، اختلالات جریان منبع و عدم تعادل ولتاژ تغذیه مجوز میدهد بطوریکه قابلیت جبران سیستم HSAPF بهبود مییابد.
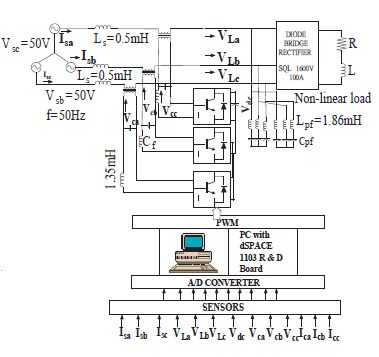
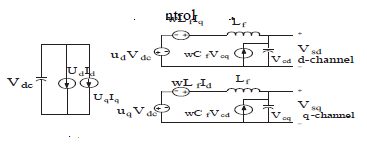
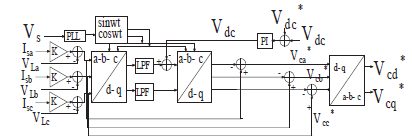
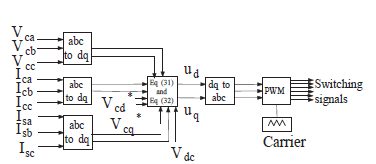
این مقاله به صورت زیر سازماندهی شده است. در بخشII، شرح شماتیک توپولوژی سیستم و ماژولهای سخت افزاری مدل HSAPF سه فاز سیستم HSAPF توضیح داده شده است. بخش III، مدلسازی متوسط سیستم HSAPF رانشان میدهد. بخش IV طراحی کنترلر برای HSAPF را آشکار میکند. بخش V نتایج خوب شبیه سازی برای جبران هارمونیک با استفاده از HSAPF را نشان میدهد. بخش VI نتایج این مقاله را ارائه میدهد.
ABSTRACT Improvement of Power Quality Using a Robust Hybrid Series Active Power Filter
The degradation in power quality causes adverse economical impact on the utilities and customers. Harmonics in current and voltage are one of the most commonly known power quality issues and are solved by the use of a hybrid series active power filter (HSAPF). In this paper, a new controller design using sliding-mode controller-2 is proposed to make the HSAPF more robust and stable. An accurate averaged model of a three-phase HSAPF is also derived in this paper. The design concept of the robust HSAPF has been verified through simulation and experimental studies, and the results obtained are discussed.
Introduction
Over the past few years, the enormous increase in the use of non-linear loads, arises many power quality issues like high current harmonics, voltage distortion and low power factor etc. on electrical grid [1]. Hence the proliferation of non-linear load in system generates harmonic currents injecting into the AC power lines. This distorted supply voltage and current causes malfunction of some protection devices, burning of transformers and motors, overheating of cables. Hence it is most important to install compensating devices for the compensation of harmonic currents and voltages produced due to nonlinear load. Traditionally, passive power filters have been used as a compensating device, to compensate distortion generated by constant non-linear loads. These filters [2] are designed to provide a low impedance path for harmonics and maintaining good power quality with an simplest design and low cost. However, passive filters have some demerits like mistuning, resonance, dependence on the conditions of the power supply system and large values of passive component that leading to bulky implementations.
For high-quality power requirements, numerous topologies of active filters i.e. APF connected in series or in parallel (series active filters and shunt active filters) to the nonlinear loads with the aim of improving voltage or current distortion. These filters are the most widely used solution, as they efficiently eliminate current distortion and the reactive power produced by non-linear loads.
But they are generally expensive and have high operating losses [3] [4]. Henceforth to overcome these drawbacks and to improve the compensation performance with reduced cost of the APFs, a novel HAPF topologyIII is introduced by Peng et al. in 1988 [5], in which APF is connected in series with the source as well as non-linear load and PPF connected in parallel with the load, which behaves as power factor correction capacitor is proposed. This topology [6] attracted much more attention to endure high load currents and works as a harmonic isolator between source and non-linear load.
The control strategy is important to enhance the performance of HSAPF. In reality, many articles for hybrid power filter have already proposed advanced techniques to reduce current harmonics created by these non-linear loads. In [7], a linear feedback-feed-forward controller is designed for hybrid power filter. But this controller is not easy for getting both steady-state and transient state performances with the linear control strategy because the dynamic model of HSAPF system contains multiplication terms of control inputs and state variables. Due to the non-linear characteristics of HSAPF, a sliding mode controller is presented in [8].
The sliding mode control is known as an appropriate control technique for controlling non-linear systems with uncertain dynamics and disturbances due to its order reduction property and low sensitivity to disturbances and plant parameter variations, which reduces the burden of the requirement of exact modeling. Furthermore, this sliding mode control also diminishes the complicacy of feedback control design by means of decoupling the system into individual subsystems of lower dimension.
Because of these given properties, the implementation of sliding mode control can be found in the areas of power electronic switching devices. The principle of sliding mode control is defined as to enforce the sliding mode motion in a predefined switching surfaces of the system state space using discontinuous control. The switching surfaces should be selected in such a way that sliding motion would maintain desired dynamics of motion according to certain performance criterion. The conventional control methods, such as Linear-quadratic regulator (LQR) [9] or Linear quadratic Gaussian (LQG) servo controller [10] for linear systems, are required to choose proper switching surfaces. Then, the discontinuous control needs to be chosen such that any states outside of the discontinuity surface are enforced to reach the surface at finite time. Accordingly, sliding mode occurs along the surface, and the system follows the desired system dynamics. The main difficulty of hardware implementation of classical sliding mode control method is chattering.
Chattering is nothing but an undesirable phenomenon of oscillation with finite frequency and amplitude. The chattering is dangerous because the system lags control accuracy, high wear of moving mechanical parts, and high heat losses occurs in electrical power circuits. Chattering occurs because of unmodeled dynamics. These unmodeled dynamics are created from servomechanisms, sensors and data processors with smaller time constants.
In sliding mode control the switching frequency should be considerably high enough to make the controller more robust, stable and no chattering because chattering reduces if switching frequency of the system increases. The application of sliding mode controller in power converter systems for example in HSAPF, a natural way to reduce chattering is increasing switching frequency.
However, it is not possible in case of power converters because of certain limitations in switching frequency for losses in power converters, for which it results in chattering. Therefore, this chattering problem cannot blame sliding mode implementation since it is mainly caused by switching limitations. In [11], it is shown that the chattering exponentially tends to zero if the relative degree of the system with actuators or sensors is two.
The relative degree of HSAPF system is two. Because of this relative degree of HSAPF system and also for these obstacles in classical sliding mode controller, this research paper proposed a new controller i.e. sliding mode controller-2. This proposed controller suppressed chattering and enhance the performance of HSAPF. This controller is completely new for this topology of HSAPF system. The recent research paper [12] focuses on carrier based PWM (CBPWM) for HSAPF topology. But in some cases the CBPWM based HSAPF may not be completely measurable in most of the real-world situations.
In case of CBPWM, power system perturbations have not been taken into consideration and also the presence of a time delay at the reference tracking point gives rise to a slow response of the overall system. Thus, tracking error is not reduced effectively and stability of the system is minimally improved. To overcome this, a SMC- 2 controller is proposed for voltage source converter (VSC). The idea behind this controller is to achieve gain stability, perfect tracking and distortion free current and load voltage. In view of above mentioned issues, we give more emphasis on the development of robust controller with a faster reference tracking approach in HSAPF, which permits all perturbations such as load voltage distortion, parametric variation of load, source current distortion and supply voltage unbalance so that compensation capability of the HSAPF system can be enhanced.
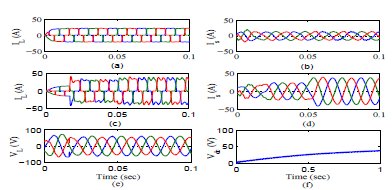
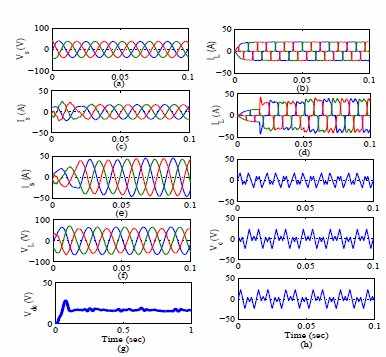
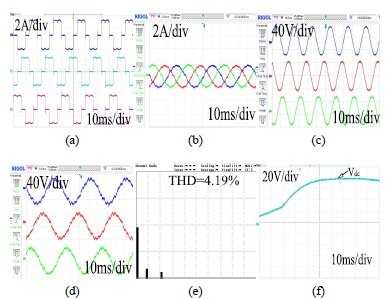
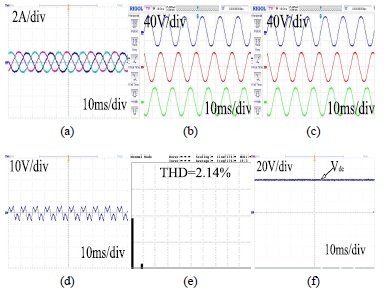
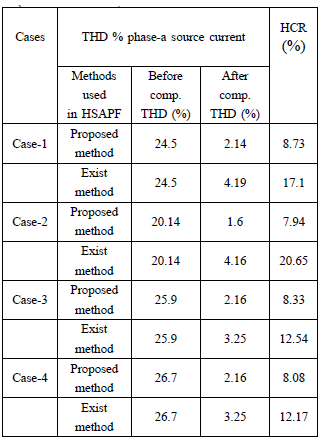
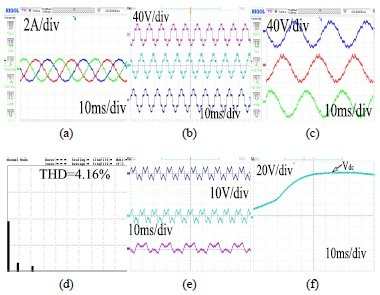
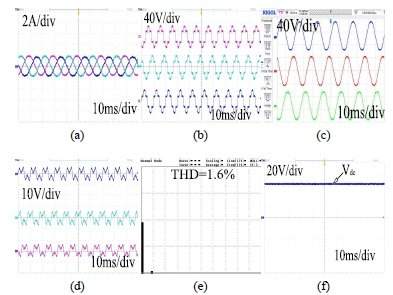
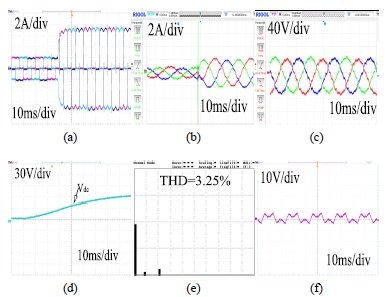
This paper is organized as follows. In section II, the description of schematic of system topology and hardware modules of three phase HSAPF model is explained. Section-III depicts the averaged modelling of HSAPF system. Section-IV disclose the controller design for HSAPF. Section-V depicts the simulation as well as experimental results for harmonic compensation using HSAPF. Section-VI presents the conclusions of this work.

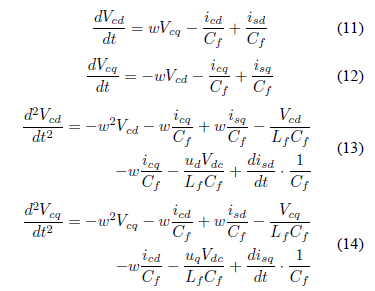
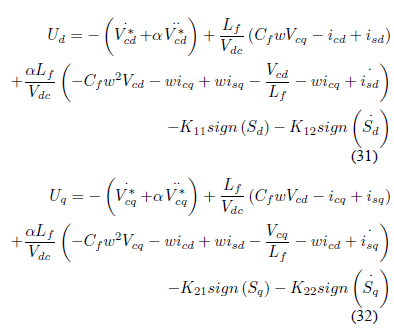

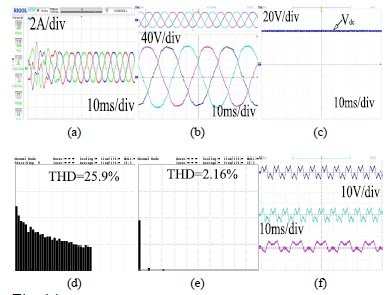
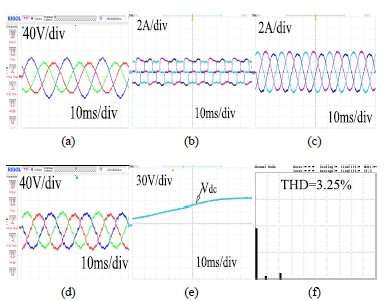
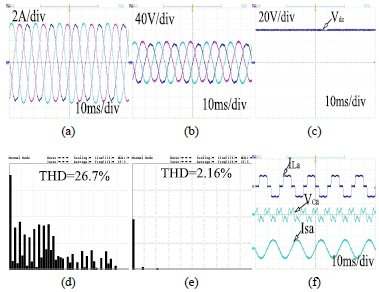
- مقاله درمورد کاربرد فیلتر توان فعال سری هیبرید (HSAPF) قوی در بهبود کیفیت توان
- ارتقا کیفیت قدرت با فیلتر توان اکتیو سری ترکیبی قوی
- بهبود کیفیت توان توسط فیلتر قدرت فعال سری ترکیبی قدرتمند
- پروژه دانشجویی کاربرد فیلتر توان فعال سری هیبرید (HSAPF) قوی در بهبود کیفیت توان
- کاربرد فیلتر توان اکتیو سری هیبرید قوی در ارتقای کیفی توان
- پایان نامه در مورد کاربرد فیلتر توان فعال سری هیبرید (HSAPF) قوی در بهبود کیفیت توان
- تحقیق درباره کاربرد فیلتر توان فعال سری هیبرید (HSAPF) قوی در بهبود کیفیت توان
- مقاله دانشجویی کاربرد فیلتر توان فعال سری هیبرید (HSAPF) قوی در بهبود کیفیت توان
- کاربرد فیلتر توان فعال سری هیبرید (HSAPF) قوی در بهبود کیفیت توان در قالب پاياننامه
- پروپوزال در مورد کاربرد فیلتر توان فعال سری هیبرید (HSAPF) قوی در بهبود کیفیت توان
- گزارش سمینار در مورد کاربرد فیلتر توان فعال سری هیبرید (HSAPF) قوی در بهبود کیفیت توان
- گزارش کارورزی درباره کاربرد فیلتر توان فعال سری هیبرید (HSAPF) قوی در بهبود کیفیت توان