پیوند هالوژنی بر اساس آنالیز توپولوژیکی لاپلاسین چگالی بار الکترونی و تفکیک انرژی


شاپا پرینت: 1610-2940 وبسایت مرجع 35 رفرنس دارد
16,500 تومانشناسه فایل: 8778
- حجم فایل ورد: 186.7KB حجم پیدیاف: 244.2KB
- فرمت: فایل Word قابل ویرایش و پرینت (DOCx)
- تعداد صفحات فارسی: 14 انگلیسی: 7
- دانشگاه:
- Laboratorio de Estructura Molecular y Propiedades, Área de Química Física, Departamento de Química, Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales y Agrimensura, Universidad Nacional del Nordeste, Avda. Libertad 5460, 3400 Corrientes, Argentina
- Facultad Regional Resistencia, Universidad Tecnológica Nacional, French 414, 3500 Resistencia, Chaco, Argentina
- ژورنال: Journal of Molecular Modeling (1)
چکیده
در این مقاله ما ماهیت برهم کنش های Cl…N را در کمپلکس هایی که بین آمونیوم استخلاف شده [NHn (x3-n) n=0, 1, 2, 3 X=-CH3, -F] به عنوان باز لوویس و مولکول F – Cl به عنوان اسید لوییس تشکیل می شود را مورد بررسی قرار داده ایم. این نمونه ها بخاطر دامنۀ وسیع تغییر انرژی پیوندی شان (BEs) برای این منظور انتخاب شده اند. محاسبات به روش اختلال مرتبه دوم مولر – پلست [(MP2/6-311++G(2d,2p] نشان داده اند که انرژی های پیوندی (BEs) برای این دسته از کمپلکس ها از 1.27Kcal/mol برای کمپلکس [F – Cl…NF3] تا 27.62Kcal/mol برای کمپلکس [F – Cl…N(CH3)3] متغیر است. توزیع بین مولکولی چگالی بار الکترونی و تابع لاپلاسین آن (L(r)=-1/4 ∇2 ρ(r در چارچوب تئوری اتم ها در مولکول (AIM) بررسی شده اند. تفکیک انرژی برهم کنش بین مولکولی نیز همچنین با روش فضای وردشی کاهش یافته (RVS) آنالیز گردیده است. تحلیل توپولوژیکی تابع (L(r نشان می دهد که خواص توپولوژیکی موضعی اندازه گیری شده در نقطه بحرانی (1+,3) [در توپولوژی (L(r] توصیفگر خوبی برای قدرت پیوند هالوژنی هستند. نتایج بدست آمده از بررسی تفکیک انرژی پیوند نشان می دهد که برهم کنش های الکترواستاتیک در پیوندهای هالوژنی نقش کلیدی بازی می کنند. از این نتایج در می یابیم که وقتی اتم هالوژنی به گروه الکترون کشنده قوی متصل می شود ، برهمکنش الکترواستاتیک بین ابر الکترونی باز لوییس و هسته هالوژنی اسید لوییس سبب تشکیل کمپلکس های هالوژنی شده و ساختار هندسی آن ها را مشخص می کند. علاوه بر این، رابطه خطی خوبی بین لگاریتم طبیعی انرژی های پیوندی و انرژی برهمکنش الکترواستاتیک بین چگالی بار الکترونی اتم نیتروژن و هسته اتم کلر وجود دارد و در تئوری AIM انرژی پتانسیل الکترواستاتیک بین این دو اتم به صورت (Ve-n (N,Cl در نظر گرفته شده است.
مقدمه مقاله
اخیرا در بین محققان علاقه زیادی برای مطالعه پیوندهای هالوژنی (XBs) دیده شده است که به دلیل خواص بی نظیر این پیوندها و توانایی بسیار بالای آن ها در زمینه های مختلف از جمله شناسایی مولکول ها، مهندسی کریستال، شیمی مولکولهای سنگین و کاربرد وسیع آن ها در گسترش ترکیبات دارویی جدید اس. مطالعه ماهیت پیوندهای هالوژنی جنبه مهمی از تحقیق و پژوهش در زمینه های ذکر شده است. مطالعه پتانسیل های الکترواستاتیک مولکول های هالوژن دار نشان می دهد که هالوژن هایی که به صورت کووالانسی با اتم های دیگر پیوند داده اند، اغلب دارای ناحیه ای با پتانسیل الکترواستاتیک مثبت در بیرونی ترین لایه اتم هالوژن در امتداد محور پیوندی D – X هستند. پولیتزر و همکارانش تشکیل پیوند هالوژنی را در برهمکنش الکترواستاتیک جاذبه بین پتانسیل مثبت و جفت الکترون تنهای اتم پذیرنده می دانند. وجود یک ناحیه با پتانسیل الکترواستاتیک مثبت روی اتم هالوژن نشان می دهد که برهم کنش های غیر کووالانسی بین اتم هالوژن و باز لوییس باید ماهیت الکترواستاتیک داشته باشد. مطالعات دیگر نشان داده اند که انرژی های دیگری غیر از انرژی الکترواستاتیک در تشکیل پیوند دخالت دارند. اخیراً Tomura سیستم های H4-nCCln…πC2H2 با n = 1, 2, 3, 4 را با روش فضای وردشی کاهش یافته (RVS) جهت اثبات این نکته که این کمپلکس ها با انرژی برهمکنش پراکندگی به پایداری رسیده اند و در کنار آن انرژی الکترواستاتیک نیز نقش مهمی در برهمکنش جاذبه بین استیلن و مولکول های کلرومتان ایفا کرده مطالعه کرده است. علاوه بر این، رایلی و همکارانش نیز ماهیت XB را با روش های محاسباتی سنگین همچون تئوری اختلال تقارن – سازگار (SAPT) بررسی کرده اند. آنها به این نتیجه رسیدند که برهمکنش بین هالومتان های فلوئورینه و بدون فلوئور و فرمالدئید هایی مثل (متانول) به انرژی الکترواستاتیک و انرژی پراکندگی بستگی خیلی زیادی دارند. با این حال در برهم کنش های برمو بنزن های استخلاف دار و نیز برمو پیریدین ها با استون، تنها نیروهای الکترواستاتیک هستند که نقش کلیدی در پایداری پیوند بازی می کنند.
آلکورتا و همکارانش در مطالعات نظری خود روی خواص منومرها، دایمرها، تریمرها و تترامرها و مولکول های هالوژن دار (ClBr. FBr. FCl) با روش تفکیک انرژی طبیعی (NEDA) دریافته اند که انرژی اصلی برهمکنش جاذبه انرژی قطبش است و در کنار آن مطالعه برهمکنش بین (Fn H3-nCBr (n=0, 1, 2, 3 و HMgH به روش MP2/aug-cc-pvtz نشان داده است که انرژی الکترواستاتیک به همراه انرژی انتقال بار و انرژی قطبش عامل اصلی پایداری این کمپلکس ها هستند.
توصیف توپولوژیکی برگرفته از تئوری کوانتومی اتم ها در مولکول (QTAIM) برای مطالعه و تشخیص پیوندهای هالوژنی بکار می روند. ژانگ و همکارانش نیز به همین روش مشخصه ها و ماهیت پیوندهای هالوژنی را در یکسری از کمپلکس های B…XY ها با B=H2S, H2CS, (CH2)2S و XY=ClF, Cl2, BrF, BrCl,Br2 مطالعه کرده اند. تحلیل توپولوژیکی این کمپلکس ها نشان داده است که این پیوندهای هالوژنی به برهم کنش های ضعیف با ماهیت الکترواستاتیک تعلق دارند. در کار قبلی، ما توپولوژی لاپلاسین توزیع چگالی بار الکترونی در پیوندهای هالوژنی آروماتیکی D–X…πC6H6 D=-H, –CN, –F, X=F, Cl را محاسبه کرده ایم. تشکیل این کمپلکس ها نتیجه برهمکنش بین چگالی بار ابر π (مولکول بنزن) و ناحیه تهی شده از بار در بخش بیرونی اتم هالوژن در امتداد محور D–X است.
با مطالعه نتایج و اطلاعات مختلف بدست آمده در مورد پیوندهای هالوژنی (XBs) می توان دریافت که ماهیت این پیوندها هنوز به درستی مشخص نشده است. ما در این پژوهش ماهیت پیوند بین اتم کلر و نیتروژن را در کمپلکس های آمونیوم استخلاف دار NHnX3-n n=0, 1, 2, 3 و X=-CH3,-F و مولکول F–Cl بررسی کرده ایم. توزیع بین مولکولی چگالی بار الکترونی و تابع لاپلاسین (L(r آن با تئوری اتم ها در مولکول (AIM) تطبیق داده شده است. این نتایج با نتایج بدست آمده از تحلیل انرژی تفکیک مرتبط هستند.
ABSTRACT Nature of halogen bonding. A study based on the topological analysis of the Laplacian of the electron charge density and an energy decomposition analysis
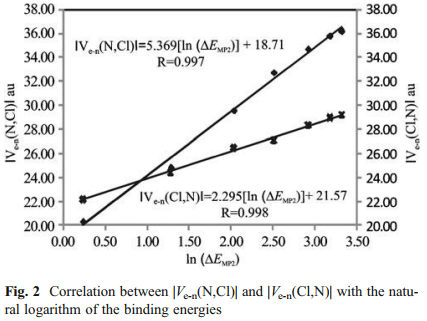
In this work we investigate the nature of the Cl···N interactions in complexes formed between substituted ammonium [NHn (x3-n) n=0, 1, 2, 3 X=-CH3, -F] as Lewis bases and F−Cl molecule as Lewis acid. They have been chosen as a study case due to the wide range of variation of their binding energies, BEs. Møller-Plesset [MP2/6-311++G(2d,2p)] calculations show that the BEs for this set of complexes lie in the range from 1.27 kcal/mol [F – Cl…NF3] to 27.62 kcal/mol [inF – Cl…N(CH3)3]. The intermolecular distribution of the electronic charge density and their (L(r)=-1/4 ∇2 ρ(r function have been investigated within the framework of the atoms in molecules (AIM) theory. The intermolecular interaction energy decomposition has also been analyzed using the reduced variational space (RVS) method. The topological analysis of the L(r) function reveals that the local topological properties measured at the (3,+1) critical point [in L(r) topology] are good descriptors of the strength of the halogen bonding interactions. The results obtained from energy decomposition analysis indicate that electrostatic interactions play a key role in these halogen bonding interactions. These results allow us to establish that, when the halogen atom is bonded to a group with high electron-withdrawing capacity, the electrostatic interaction between the electron cloud of the Lewis base and the halogen atom unprotected nucleus of the Lewis acid produces the formation and determines the geometry of the halogen bonded complexes. In addition, a good linear relationship has been established between: the natural logarithm of the BEs and the electrostatic interaction energy between electron charge distribution of N atom and nucleus of Cl atom, denoted as Ve-n (N,Cl) within the AIM theory.
Introduction
There has recently been an increasing interest in halogen bonds, XBs, because of their unique properties and their tremendous potential in the fields of molecular recognition, crystal engineering, supramolecular chemistry and the development of new pharmaceutical compounds. The study of the nature of halogen bonding interactions has turned out to be an important aspect of this topic. Studies of the electrostatic potentials of halogen-containing molecules show that the atoms of a halogen covalently bound often have a region of positive electrostatic potential on the outermost portion of the halogen atom, centered on the extension of the D−X bond [1–4]. Politzer et al. have attributed the formation of halogen bonds to the attractive electrostatic interaction between this positive potential and a lone pair of the acceptor. The presence of a region with positive electrostatic potential on a halogen indicates that noncovalent interactions between that halogen and a Lewis base should be highly electrostatic in nature. However, there are several studies showing that other components of the interaction energy can be decisive. Recently, Tomura [5] has studied the H4-nCCln…πC2H2 (with n01, 2, 3, 4) systems by RVS method [6], finding that these complexes are mainly stabilized by the dispersion interaction while the electrostatic interaction also plays an important role in the attraction between acetylene and chloromethane molecules. Moreover, Riley et al. [7] have investigated the nature of the XBs using high-level computational methods, including the symmetry-adapted perturbation theory (SAPT) [8]. These authors have found that, the interactions between fluorinated and nonfluorinated halomethanes with formaldehyde (as well as with methanol) depend strongly on the electrostatic contributions as well as on the dispersion. However, in the interactions of substituted bromobenzenes and bromopyrimidines with acetone, only the electrostatic forces play the key role.
Alkorta et al. [9], in their theoretical study of the properties of the monomers, dimers, trimers, and tetramers of the inter halogen molecules (FCl, FBr, and ClBr) using the natural energy decomposition analysis (NEDA) [10] have found that the main source of the interaction energy corresponds to the polarization term. In addition, the study of the interactions between Fn H3-nCBr (with n=0, 1, 2, 3) and HMgH at the MP2/aug-cc-pVTZ level has revealed that the electrostatic interaction together with the charge transfer and polarization interactions, are responsible for the stability of these complexes [11].
The topological description derived from the quantum theory of atoms in molecules (QTAIM) [12–14] has been extensively applied to study and characterizes the halogen bonding interactions [15–22]. Using this methodology, Zhang et al. [23] have recently studied the characteristics and nature of the halogen bonding in a series of B···XY with B=H2S, H2CS, (CH2)2S and XY=ClF, Cl2, BrF, BrCl,Br2, Br2] complexes. Their topological analysis has demonstrated that these halogen bonding interactions belong to weak interactions with an electrostatic nature. In a previous work, we have analyzed the Laplacian topology of the electronic charge density distribution in the aromatic halogen bonds D–X…πC6H6 (with D 0−H, −CN, −F and X 0F, Cl) [24]. The formation of these complexes results from the interaction between the charge density provided by the π- cloud (benzene molecule) and the charge density depletion region localized at the outer region of the halogen atom in the direction of the D−X bond.
In view of the existing information, it is clear that the nature of the XBs has not yet been elucidated. In order to make a contribution, in this work we investigate the nature of the bonding between chorine and nitrogen atoms in complexes formed by substituted ammonium [NHnX3-n (with n=0, 1, 2, 3 and X0−CH3,−F] with F−Cl molecule. The intermolecular distribution of both the electronic charge density and the L(r) function, has been examined within the framework of the AIM theory. These results are related to those obtained by the decomposition energy analysis.

- مقاله درمورد پیوند هالوژنی بر اساس آنالیز توپولوژیکی لاپلاسین چگالی بار الکترونی و تفکیک انرژی
- طبیعت اتصال هالوژن. مطالعه بر اساس تجزیه توپولوژیکی لاپلایس چگالی بار الکترون و تجزیه تجزیه انرژی
- پروژه دانشجویی پیوند هالوژنی بر اساس آنالیز توپولوژیکی لاپلاسین چگالی بار الکترونی و تفکیک انرژی
- آنالیز توپولوژیکی لاپلاسین دانسیته بار الکترونی و تحلیل تفکیک انرژی
- پایان نامه در مورد پیوند هالوژنی بر اساس آنالیز توپولوژیکی لاپلاسین چگالی بار الکترونی و تفکیک انرژی
- تحقیق درباره پیوند هالوژنی بر اساس آنالیز توپولوژیکی لاپلاسین چگالی بار الکترونی و تفکیک انرژی
- مقاله دانشجویی پیوند هالوژنی بر اساس آنالیز توپولوژیکی لاپلاسین چگالی بار الکترونی و تفکیک انرژی
- پیوند هالوژنی بر اساس آنالیز توپولوژیکی لاپلاسین چگالی بار الکترونی و تفکیک انرژی در قالب پاياننامه
- پروپوزال در مورد پیوند هالوژنی بر اساس آنالیز توپولوژیکی لاپلاسین چگالی بار الکترونی و تفکیک انرژی
- گزارش سمینار در مورد پیوند هالوژنی بر اساس آنالیز توپولوژیکی لاپلاسین چگالی بار الکترونی و تفکیک انرژی
- گزارش کارورزی درباره پیوند هالوژنی بر اساس آنالیز توپولوژیکی لاپلاسین چگالی بار الکترونی و تفکیک انرژی