تاثیر لاتکس کوپلیمر استایرن و بوتادین بر دوام بستر جاده تثبیت شده با افزودنی سیمان پرتلند

21,500 تومانشناسه فایل: 7907
- حجم فایل ورد: 543KB حجم پیدیاف: 208.6KB
- فرمت: فایل Word قابل ویرایش و پرینت (DOCx)
- تعداد صفحات فارسی: 27 انگلیسی: 10
- دانشگاه:
- Sustainable Urban Transport Research Centre (SUTRA), Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Malaysia
- Department of Civil and Structural Engineering, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Malaysia
- Department of Civil Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, University of Malaya, Malaysia
- ژورنال: Construction and Building Materials (6)
چکیده
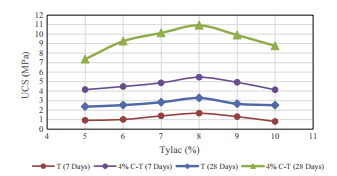
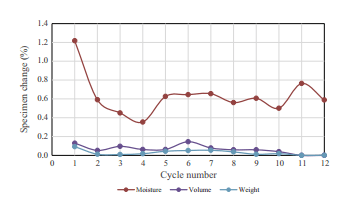
این تحقیق اثر نوع و مقدار سیمان پرتلند و امولسیون استایرن – بوتادین (Tylac® 4190) بر عملکرد کوتاه مدت یک لایه از بستر جاده از طریق ارزیابی آزمایشگاهی از مخلوط های تثبیت شده مصالح خاک را بررسی می کند. نمونه های استوانه ای تثبیت شده با سیمان پرتلند (0-6%)، Tylac® 4190 (5-10%)، و ترکیبی از هر دوی این مواد افزودنی مدلسازی شد، برای 7، 28، و 60 روز سخت شده و پس از آن تحت توالی تنش های مختلف قرار گرفت تا مقاومت فشاری ساده، مقاومت کششی غیر مستقیم، و ضریب ارتجاعی کششی غیر مستقیم بررسی شود. عملکرد بلند مدت (دوام) نمونه ای مصالح خاک از طریق انجام آزمون های چرخه ای خیس کردن و خشک کردن (WD) در زمان 7 روز گیرش بر نمونه های مصالح خاک تثبیت شده با سیمان و Tylac® 4109 مورد بررسی قرار گرفت. نتایج نشان داد که افزودنی ها مقاومت نمونه ها را بهبود می بخشد، که نشان می دهد این شاخص کیفیتی مهمی از ویژگی های مکانیکی بستر جاده است. نتایج آزمون های انجام شده برای ارزیابی مقاومت نمونه ها نسبت به چرخه WD نشان داد که افزودن مخلوط 4% سیمان پرتلند – 8% Tylac® 4109 منجر به کاهش 86/99% در جذب آب و نفوذ پذیری، تغییرات حجمی 88.55%، و تغییرات وزنی 92.84% نسبت به نمونه ای با تنها 4% سیمان، بعد از 12 بار چرخه WD می شود. این مقاله همچنین یافته های مطالعات مرتبط انجام شده برای تعیین تاثیرات متغیرهای موثر با استفاده از تحلیل رگرسیون غیرخطی برای ایجاد مدل های پیش بینی قابل توجه برای مقاومت بر اساس پارامترهای مخلوط را ارائه می دهد.
مقدمه مقاله
فاکتورهایی مانند افزایش تعداد وسایل نقلیه، حجم ترافیکی، و فشار باد تایر، مهندسان جاده را بر آن داشت تا تکنولوژی های بهتری را برای افزایش ظرفیت تحمل بار جاده و بهبودی عملکردهای بلند مدت و کوتاه مدت جاده توسعه دهند. انواعی از خاک ها یا مواد گرانولی برای ساخت بسترهای جاده در دسترس هستند، اما آنها ممکن است ویژگی های ناکافی همانند ظرفیت تحمل بار پایین، حساسیت نسبت به آسیب رطوبت، و حساسیت نسبت به شرایط محیطی را نشان دهند، که به نوبه ی خود منجر به تخریب قابل توجه جاده و کوتاه شدن عمر جاده می شود. با این حال، افزودن عامل تثبیت کننده می تواند ویژگی های مخلوط مصالح خاک را بهبود بخشد. تثبیت کننده های مصالح خاک بطور سنتی یا غیر سنتی طبقه بندی می شوند. افزودنی های سنتی شامل سیمان، آهک، خاکستر، و مصالح بتمنس می شود، درحالیکه افزودنی های غیرسنتی شامل آنزیم ها، پلیمرهای مایع، رزین، اسیدها، سیلیکات، یون ها، و مشتقات لیگنین می شود. در میان این مصالح تثبیت کننده مختلف، بستر اصلاح شده با سیمان (CTB) سفتی و مقاومت قابل توجه زیادی را نشان می دهد و هنگامی که برای ساخت جاده استفاده شوند قابلیت استفاده خوب و دوام بالایی را نشان می دهد. تثبیت سازی سیمان از خاک بر مبنای آزمایشی در سال 1917 آغاز شد، و پس از آن آثار متعددی در مورد این موضوع منتشر شد [1-6]. تثبیت کننده های پلیمری معمولا استات وینیل یا کوپلیمرهای اکریلیک واقع شده در امولسیون از طریق سورفاکتانت هستند. تثبیت کننده پلیمر ذرات مصالح خاک را اندود می کند، و همبندهای فیزیکی شکل می گیرد، هنگامیکه امولسیون آب تبخیر شود، و یک مخلوط پلیمر- خاک باقی می ماند. عامل امولسیون می تواند همچنین به عنوان سورفکتانت عمل کند، و نفوذ برای کاربردهای موضعی و اندود شدن ذرات تحت شرایط آمیختن را بهبود بخشد. استفاده از پلیمرها به عنوان اصلاح کننده ها در ساختار جدید به نظر می رسد استراتژی امیدوارکننده ای برای بهبودی ریزساختار مخلوط ها و افزایش دهنده ی دوام آنها باشد [7-11]. پلیمرها دارای تاثیر قابل توجهی بر ویژگی های کارایی و مکانیکی مخلوط سیمان – مصالح خاک هستند. ادبیات پیشینه معمولا به مواد پلیمری استایرن- بوتادین معمولا استفاده شده اشاره دارند. معروف است که این مواد نسبت به بتن معمولی مبتنی بر سیمان پرتلند دارای دوام عالی هستند، و نسبت به حمله اسیدی، ذوب شدن یخ زدگی، و انتشار کلرید مقاوم هستند. نویسندگان متعددی نشان داده اند که اشباع پلیمری از مواد سیمانی- مصالح خاک ممکن است منجر به افزایش دوام بسته به نوع پلیمرهای استفاده شده شود. مطالعات قبلی همچنین نشان داده اند که ترکیب لاتکس امولسیون استایرن – بوتادین (SBE) درون یک مخلوط سبب افزایش مقاومت آن نسبت به نفوذ یون کلرید می شود [10، 12-16]. ساختار مولکولی امولسیون استایرن – بوتادین (SBE) شامل زنجیره های منعطف بوتادین و زنجیره های سخت استارین می شود، که ترکیب آنها سبب ویژگی های مطلوب برای مواد سیمان- مصالح خاک اصلاح شده با SBE می شود، مانند ویژگی های مکانیکی خوب، سفتی و تنگی آب، و مقاومت در برابر سایش [12، 17-20]. یک بستر اصلاح شده با امولسیون استایرن – بوتادین با سیمان (CSBETB) می تواند راه حل های مقرون به صرفه ای را برای بسیاری از طراحی های رایج و سناریوهای ساخت فراهم آورد و سبب مقاومت و پشتیبانی اضافی بدون افزایش ضخامت کلی لایه های جاده شود. بسته به الزامات یک پروژه، CSBETB می تواند سرعت ساخت را افزایش دهد و ظرفیت ساختاری جاده را بهبود بخشد. علاوه بر این، یک بستر سفت تر به سبب بار ترافیکی سنگین سبب کاهش تغییر شکل می شود، در نتیجه عمر جاده افزایش می یابد [4، 21-27]. CSBETB می تواند همچنین بارها را بر روی منطقه گسترده ای توزیع سازد و تنش بر روی قشر بستر جاده را کاهش دهد. آن دارای ظرفیت حمل بار بالایی است، و تحت بار بیشتر محکم نمی شود، شیار در جاده های آسفالتی آغشته گرم را کاهش می دهد، و نسبت به تخریب یخ زدن – آب شدن و خیس شدن – خشک شدن مقاوم است [28-30]. هدف تحقیق کنونی ارزیابی عوامل تاثیر گذار بر عملکرد و مقاومت بستر اصلاح شده با سیمان – Tylac 4109 (CTTB) از طریق آزمون های آزمایشگاهی بود تا مقاومت فشاری ساده (UCS)، مقاومت کششی غیرمستقیم (ITS)، و ضریب ارتجاعی کششیی غیر مستقیم (ITRM)، و همچنین آزمون های چرخه خیس شدن و خشک شدن (WD) تعیین شود، که عواملی هستند که اغلب برای ارزیابی میزان تثبیت سازی جاده (RBS) استفاده می شوند. هدف دیگر این مقاله تعیین محتوای مطلوب سیمان پرتلند و Tylac 4190 در مخلوط آن ها بود. آخرین اما مهمترین هدف این مقاله مقایسه تاثیر این دو مواده افزودنی بر مخلوط مصالح –خاک با استفاده از مدل های پیش بینی قابل توجه بود.
ABSTRACT Effect of styrene–butadiene copolymer latex on properties and durability of road base stabilized with Portland cement additive
This study investigated the effects of the type and amount of Portland cement and carboxylated styrene–butadiene emulsion (Tylac® 4190) on the short-term performance of a road base layer via a laboratory evaluation of stabilized soil-aggregate mixtures. Cylindrical specimens stabilized with Portland cement (0–6%), Tylac® 4190 (5–10%), and a mixture of both these additives were molded, cured for 7, 28, and 60 days, and then subjected to different stress sequences to study the unconfined compressive strength, indirect tensile strength, and indirect tensile resilient modulus. The long-term performance (durability) of stabilized soil-aggregate specimens was investigated by conducting wetting and drying (WD) cycling tests on 7-day-cured soil-aggregate specimens stabilized with cement and Tylac® 4190. The results revealed that the additives improved the strength of the specimens, which has been found to be an important quality indicator of road base mechanical properties. Results of tests conducted to assess the specimens’ resistance to WD cycling showed that the addition of a 4% Portland cement–8% Tylac® 4190 mixture resulted in reductions of 86.99% in both water absorption and permeability, volume changes of 88.55%, and weight changes of 92.84% relative to a sample with only 4% cement after 12 WD cycles. This paper also presents the findings of a correlation study conducted for determining the influences of affective variables using nonlinear regression analysis to establish significant prediction models for strength based on mixture parameters.
Introduction
Factors such as an increased number of vehicles, traffic loading, and tire pressure have motivated pavement engineers to develop better technologies for increasing the pavement bearing capacity and improving short-term and long-term pavement performances. A variety of soils or granular materials are available for the construction of road bases, but they may exhibit inadequate properties, e.g., low bearing capacity, susceptibility to moisture damage, and susceptibility to environmental conditions, which would in turn result in substantial pavement distress and shortening of pavement life. However, the addition of a stabilizing agent can improve the properties of a soil-aggregate mixture. Soil-aggregate stabilizers are categorized as either traditional or nontraditional. Traditional additives include cement, lime, fly ash, and bituminous materials, whereas nontraditional additives include enzymes, liquid polymers, resins, acids, silicates, ions, and lignin derivatives. Among these different stabilizing materials, cement-treated base (CTB) develops significantly high stiffness and strength and exhibits good serviceability and high durability when used for pavement construction. Cement stabilization of soil was initiated on a trial basis in 1917, and since then, several works have been published on this topic [1–6]. Polymer stabilizers are typically vinyl acetates or acrylic copolymers suspended in an emulsion by surfactants. The polymer stabilizer coats soil-aggregate particles, and physical bonds are formed when the emulsion water evaporates, leaving a soil–polymer matrix. The emulsifying agent can also serve as a surfactant, improving penetration for topical applications and particle coating under admix conditions. The use of polymers as modifiers in new structures seems to be a promising strategy for improving the microstructure of mixtures and enhancing their durability [7–11]. Polymers have a significant effect on the workability and mechanical properties of soil aggregate–cement mixture. The literature usually refers to the more commonly used styrene–butadiene polymer materials. These materials are known to possess superior durability over ordinary Portland-cement-based concrete, and are resistant to acid attack, ice melting, and chloride diffusion. Several authors have shown that polymer impregnation of soil aggregate–cement materials may lead to increased durability depending on the type of polymers used. Previous studies have also indicated that the admixing of styrene–butadiene emulsion (SBE) latex into a mixture improved its resistance to chloride-ion penetration [10,12–16]. The molecular structure of SBE includes both flexible butadiene chains and rigid styrene chains, the combination of which lends many desirable characteristics to SBE-modified soil aggregate–cement materials, such as good mechanical properties, water tightness, and abrasion resistance [12,17–20]. A cement– SBE-treated base (CSBETB) can provide cost-effective solutions to many common designs and construction scenarios and impart additional strength and support without increasing the total thickness of the pavement layers. Depending on the requirements of a project, CSBETB can increase the construction speed and enhance the structural capacity of the pavement. In addition, a stiffer base reduces deflections due to heavy traffic loads, thereby extending pavement life [4,21–27]. CSBETB can also distribute loads over a wider area and reduce the stresses on the subgrade. It has a high load-carrying capacity, does not consolidate further under load, reduces rutting in hot-mix asphalt pavements, and is resistant to freeze–thaw and wetting–drying (WD) deterioration [28–30]. The goal of the present work was to assess the factors affecting the performance and strength of Cement–Tylac 4190 treated base (CTTB) via laboratory tests aimed at determining its unconfined compressive strength (UCS), indirect tensile strength (ITS), and indirect tensile resilient modulus (ITRM), as well as WD cycling tests, which are the most frequently employed factors for assessing the degree of road base stabilization (RBS). Another goal was to determine the optimum contents of Portland cement and Tylac 4190 in their mixture. The last but most important goal of the work was to compare the effects of these two additives on the soil-aggregate mixtures using significant prediction models.
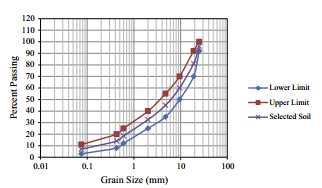
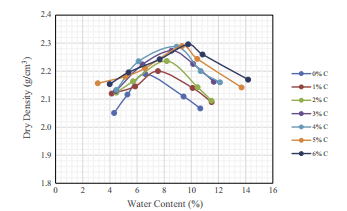
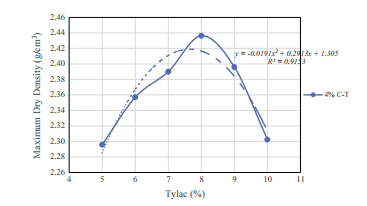
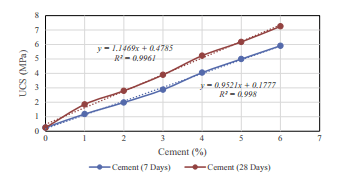
- مقاله درمورد تاثیر لاتکس کوپلیمر استایرن و بوتادین بر دوام بستر جاده تثبیت شده با افزودنی سیمان پرتلند
- اثر لاتکس کوپلیمر استایرن و بوتادین بر خواص و دوام پایه جاده تثبیت شده با افزودنی سیمان پرتلند
- پروژه دانشجویی تاثیر لاتکس کوپلیمر استایرن و بوتادین بر دوام بستر جاده تثبیت شده با افزودنی سیمان پرتلند
- اثر لاتکس کوپلیمر استارین بوتادین بر ویژگی بستر جاده
- پایان نامه در مورد تاثیر لاتکس کوپلیمر استایرن و بوتادین بر دوام بستر جاده تثبیت شده با افزودنی سیمان پرتلند
- تحقیق درباره تاثیر لاتکس کوپلیمر استایرن و بوتادین بر دوام بستر جاده تثبیت شده با افزودنی سیمان پرتلند
- مقاله دانشجویی تاثیر لاتکس کوپلیمر استایرن و بوتادین بر دوام بستر جاده تثبیت شده با افزودنی سیمان پرتلند
- تاثیر لاتکس کوپلیمر استایرن و بوتادین بر دوام بستر جاده تثبیت شده با افزودنی سیمان پرتلند در قالب پاياننامه
- پروپوزال در مورد تاثیر لاتکس کوپلیمر استایرن و بوتادین بر دوام بستر جاده تثبیت شده با افزودنی سیمان پرتلند
- گزارش سمینار در مورد تاثیر لاتکس کوپلیمر استایرن و بوتادین بر دوام بستر جاده تثبیت شده با افزودنی سیمان پرتلند
- گزارش کارورزی درباره تاثیر لاتکس کوپلیمر استایرن و بوتادین بر دوام بستر جاده تثبیت شده با افزودنی سیمان پرتلند