نقش آنزیم های میکروبی در اصلاح آلودگی های زیست محیطی

18,600 تومانشناسه فایل: 7664
- حجم فایل ورد: 333.3KB حجم پیدیاف: 568.7KB
- فرمت: فایل Word قابل ویرایش و پرینت (DOCx)
- تعداد صفحات فارسی: 19 انگلیسی: 12
- دانشگاه:Department of Biochemistry, Bangalore University, Bangalore 560001, India
- ژورنال: Enzyme Research (1)
چکیده
تعداد زیادی از آنزیم های تولید شده از باکتری ها – قارچ ها و گیاهان وظیفه تجزیه آلاینده های ارگانیک را دارند. اصلاح زیستی یک بیوتکنولوژی مقرون به صرفه و خواهان محیط زیست می باشد که توسط آنزیم های میکروبی تقویت می شود. فعالیت های تحقیقی در این حوزه با فرایندهای رو به توسعه برای کاهش میزان سمیت آلاینده و دست یابی به مواد مفید در ارتباط هستند. اطلاعات به دست آمده از مکانیزم های آنزیم های اصلاح زیستی مثل هیدرولازها و اکسیدوردوکتاز ها به صورت گسترده بررسی شده اند. در این مقاله تلاش شده است تا اطلاعات توصیفی در مورد آنزیم های میکرو ارگان های مختلف موجود در تجزیه آلاینده ها – کاربردها و پیشنهادات و محدودیت های مرتبط شرح داده شوند.
مقدمه مقاله
کیفیت زندگی در روی زمین با کیفیت نهایی محیط در ارتباط است.متاسفانه ، پیشرفت علم – فناوری و صنعت در فاضلاب ها و ضایعات هسته ای امکان اختلال در اکوسیستم را فراهم آورده اند و بنابراین یک مسئله جدی برای بقای انسان در کره زمین شده اند. در گذشته، ضایعات با حفر یک گودال و پرکردن آن منهدم می شدند. ثبات این حالت انهدام به علت نیاز به مکان های جدید برای حفاری کار دشواری می باشد.
فناوری های جدید انهدام ضایعات که از تجزیه شیمیایی و حرارت بالا استفاده می کنند نیز تکامل یافته اند . اگر چه این روش ها می توانند در کاهش آلایندگی موثر باشند ، اما معایبی هم دارند. این روش ها پیچیده – غیر اقتصادی و فاقد پذیرش عمومی هستند .تلاشها برای رفع این معایب متمرکز بر استفاده از روش های اصلاح زیستی به عنوان یک روش جایگزین می باشند.
اصلاح زیستی یک روش تجزیه آلاینده مواد خطرناک و نیمه خطرناک است.استفاده از موجودات میکروسکوپی مختلف مثل باکتری ها – قارچ ها –جلبک ها و گیاهان برای اصلاح زیستی آلاینده ها نیز گزارش شده است.وجود گیاهان در تجزیه آلاینده ها ،اصلاح فیتوزیستی نامیده می شود که این فرایند یک فناوری سبز است که باعث سهولت در حذف یا تجزیه مواد شیمیایی سمی در خاک – رسوبات – آب های زیرزمینی – آب های سطحی و هوا می شود. از نظر ژنتیکی ، گیاهان مهندسی شده هم مورد استفاده قرار می گیرند.برای مثال ، آرسنیک توسط گیاهانی چجون آرابیوسیز تالیانا اصلاح می شود که دو باکتری را مهار می کند. یکی ار ژن ها امکان اصلاح آرسنات به آرسنیت را فراهم می آورد و ژن دوم هم آرسنیت اصلاح شده را پیوند می دهد و در حفره ها ذخیره می کند.
فرایند اصلاح زیستی عمدتا بستگی به میکرو ارگان هایی دارد که به آلاینده ها حمله می کنند و آنها را به مواد تجزیه پذیر تبدیل می کنند . از آنجایی که اصلاح زیستی فقط در شرایط محیطی امکان رشد و فعالیت میکروب را فراهم می آورند ، کاربرد آن شامل ایجاد تغییر در پارامترهای محیطی برای رشد و تجزیه میکروبی می شود (شکل 1).
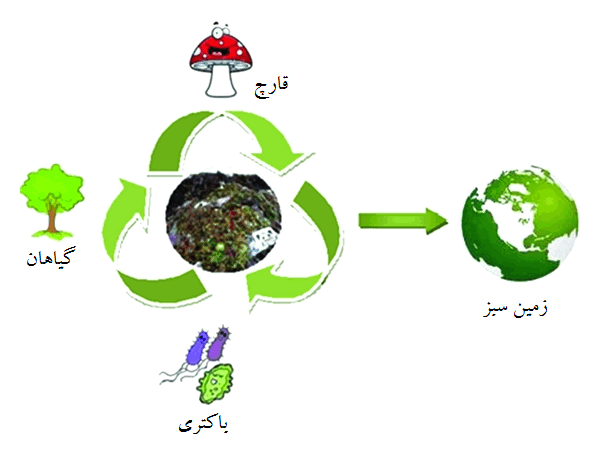
فرایند اصلاح زیستی یک فرایند بسیار کند است و فقط گونه های خاصی از باکتری ها و قارچ ها توانایی تجزیه آلاینده ها را دارند. بسیاری از رشته های قارچی هم به عنوان عامل اصلاح زیستی موثر هستند اما تاثیر آنها فقط در شرایط آزمایشگاهی است.محدود کردن رشد باکتری تحت تاثیر میزان PH- دما –اکسیژن – ساختار خاک – رطوبت و میزان مواد غذایی و فعالیت ضعیف آلاینده ها قرار می گیرند. اگر چه موجودات میکروسکوپی می توانند در محیط های متعددی وجود داشته باشند ، اما بسیاری از آنها شرایط بهینه را شرایط خارج آزمایشگاه می دانند. بسیاری از سیستم های اصلاح زیستی در شرایط هوازی عمل می کنند اما محیط های غیرهوازی هم امکان تجزیه میکروبی را فراهم می آورند. هم باکتری و هم قارچ متمرکز بر آنزیم های مختلف داخل سلول و خارج از سلول برای اصلاح آلاینده ها هستند.
ABSTRACT Role of Microbial Enzymes in the Bioremediation of Pollutants: A Review
A large number of enzymes from bacteria, fungi, and plants have been reported to be involved in the biodegradation of toxic organic pollutants. Bioremediation is a cost effective and nature friendly biotechnology that is powered by microbial enzymes. The research activity in this area would contribute towards developing advanced bioprocess technology to reduce the toxicity of the pollutants and also to obtain novel useful substances. The information on the mechanisms of bioremediation-related enzymes such as oxidoreductases and hydrolases have been extensively studied. This review attempts to provide descriptive information on the enzymes from various microorganisms involved in the biodegradation of wide range of pollutants, applications, and suggestions required to overcome the limitations of their efficient use.
Introduction
The quality of life on the Earth is linked inextricably to the overall quality of the environment. Unfortunately the progress in science, technology, and industry a large amount ranging from raw sewage to nuclear waste is let out or dumped into the ecosystem thereby posing a serious problem for survival of mankind itself on earth.
In the past, wastes were traditionally disposed by digging a hole and filling it with waste material. This mode of waste disposal was difficult to sustain owing to lack of new place every time to dump. New technologies for waste disposal that use high-temperature incineration and chemical decomposition (e.g., base-catalyzed dechlorination, UV oxidation) have evolved. Although they can be very effective at reducing wide a range of contaminants but at the same time have several drawbacks. These methods are complex, uneconomical, and lack public acceptance. The associated deficiencies in these methods have focused efforts towards harnessing modern-day bioremediation process as a suitable alternative.
Bioremediation is a microorganism mediated transformation or degradation of contaminants into nonhazardous or less-hazardous substances. The employability of various organisms like bacteria, fungi, algae, and plants for efficient bioremediation of pollutants has been reported [1, 2]. The involvement of plants in the bioremediation of pollutants is called as phytoremediation. The process of phytoremediation is an emerging green technology that facilitates the removal or degradation of the toxic chemicals in soils, sediments, groundwater, surface water, and air (RTDF). Genetically, engineered plants are also in use. For instance arsenic is phytoremediated by genetically modified plants such as Arabidopsis thaliana which expresses two bacterial genes. One of these genes allows the plant to modify arsenate into arsenite and the second one binds the modified arsenite and stores it in the vacuoles [2].
The process of bioremediation mainly depends on microorganisms which enzymatically attack the pollutants and convert them to innocuous products. As bioremediation can be effective only where environmental conditions permit microbial growth and activity, its application often involves the manipulation of environmental parameters to allow microbial growth and degradation to proceed at a faster rate (Figure 1).
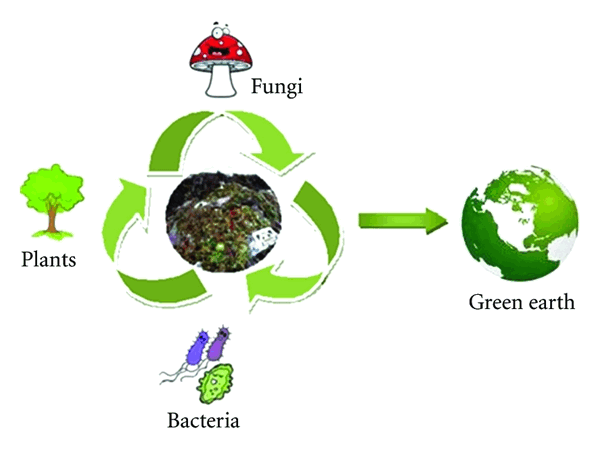
The process of bioremediation is a very slow process. Only certain species of bacteria and fungi have proven their ability as potent pollutant degraders. Many strains are known to be effective as bioremediation agents but only under laboratory conditions. The limitation of bacterial growth is under the influence of pH, temperature, oxygen, soil structure, moisture and appropriate level of nutrients, poor bioavailability of contaminants, and presence of other toxic compounds. Although microorganisms can exist in extreme environment, most of them prefer optimal condition a situation that is difficult to achieve outside the laboratory [1, 3–5]. Most bioremediation systems operate under aerobic conditions, but anaerobic environments may also permit microbial degradation of recalcitrant molecules. Both bacteria and fungi rely on the participation of different intracellular and extracellular enzymes respectively for the remediation of recalcitrant and lignin and organopollutants [1, 6].
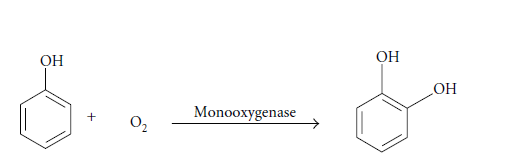


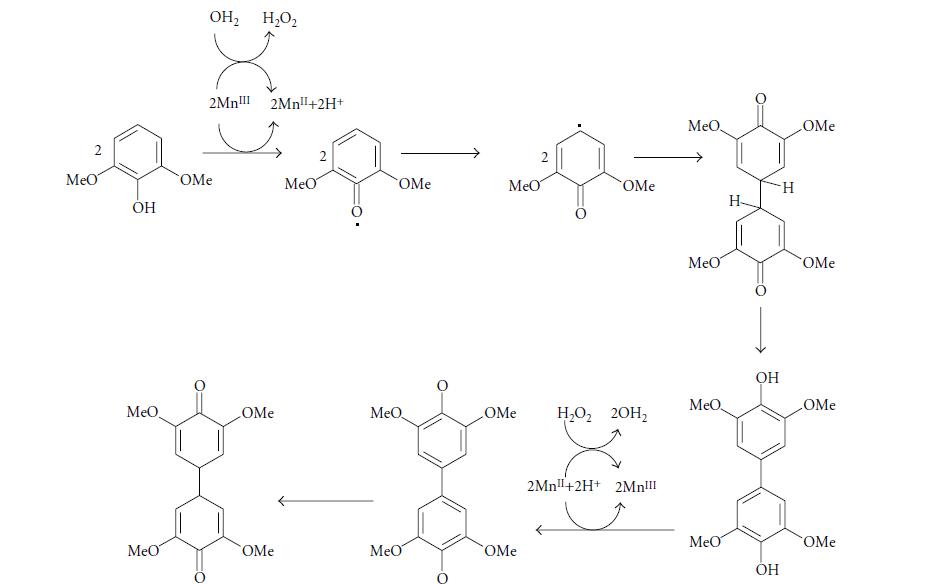

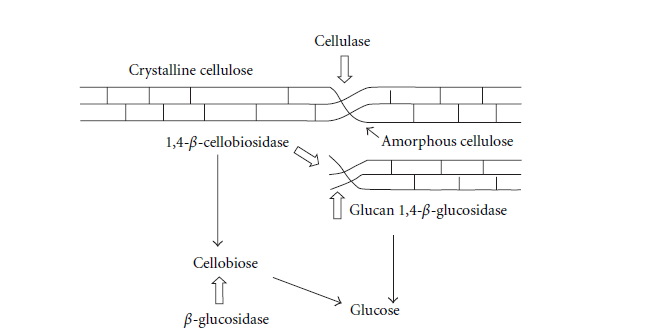
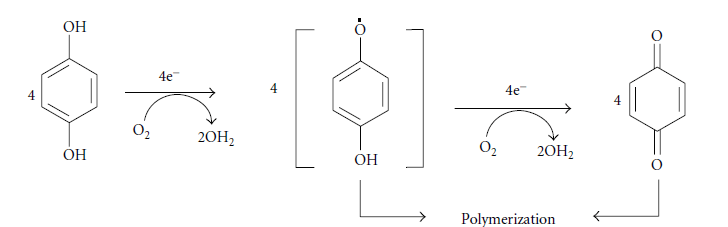
- مقاله درمورد نقش آنزیم های میکروبی در اصلاح آلودگی های زیست محیطی
- نقش آنزیم های میکروبی در برآورده کردن آلودگی های زیست محیطی: یک مرور
- نقش میکروبی آنزیم در زیست پالایی آلاینده: مروری
- پروژه دانشجویی نقش آنزیم های میکروبی در اصلاح آلودگی های زیست محیطی
- نقش آنزیم های میکروبی در بهبود زیست محیطی آلوده کننده
- پایان نامه در مورد نقش آنزیم های میکروبی در اصلاح آلودگی های زیست محیطی
- تحقیق درباره نقش آنزیم های میکروبی در اصلاح آلودگی های زیست محیطی
- مقاله دانشجویی نقش آنزیم های میکروبی در اصلاح آلودگی های زیست محیطی
- نقش آنزیم های میکروبی در اصلاح آلودگی های زیست محیطی در قالب پاياننامه
- پروپوزال در مورد نقش آنزیم های میکروبی در اصلاح آلودگی های زیست محیطی
- گزارش سمینار در مورد نقش آنزیم های میکروبی در اصلاح آلودگی های زیست محیطی
- گزارش کارورزی درباره نقش آنزیم های میکروبی در اصلاح آلودگی های زیست محیطی